Search
Search for projects by name or address
 Gnosis Bridge
Gnosis Bridge
L2BEAT Bridges is a work in progress. You might find incomplete research or inconsistent naming. Join our Discord to suggest improvements!
About
Gnosis Bridge unites the former token bridges Omnibridge and xDai bridge as the official bridge between Gnosis Chain and Ethereum.
About
Gnosis Bridge unites the former token bridges Omnibridge and xDai bridge as the official bridge between Gnosis Chain and Ethereum.
Gnosis canonical bridges paused
2025 Nov 3rd
Bridging out from Gnosis Chain has been temporarily halted following the Balancer V2 exploit.
Plonky3 vulnerability patch
2025 Jun 4th
SP1 verifier is patched to fix critical vulnerability in Plonky3 proof system (SP1 dependency).
It uses a set of trusted validators to verify deposits for lock-mint bridging. Tokens sent to the bridge escrow can be further sent to yield generating contracts (e.g. AAVE, Spark) by permissioned actors to accrue interest.
Funds can be stolen if
Funds can be frozen if
Users can be censored if
Principle of operation
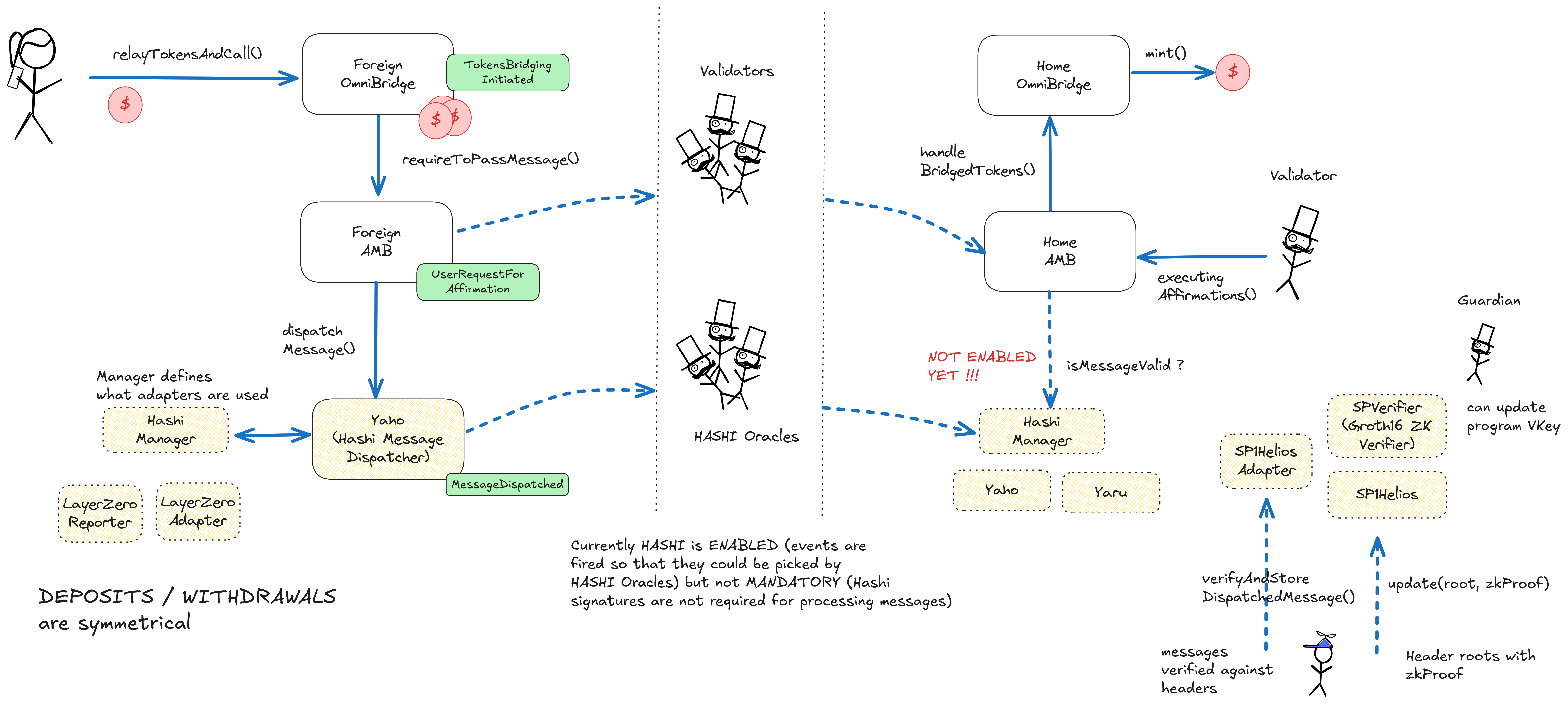
The Gnosis bridge is comprised of two standard multisig-validated token bridges (Omni and xDAI) with similar architecture and validators. While the xDAI bridge is only used for bridging USDS-related tokens (xDAI is Gnosis Chains gas token), the Omni bridge can be used to bridge many other ERC-20 tokens. Both bridges on ethereum are served by external validators that sign bridge messages via custom multisigs. Assets that are locked in one of the escrows on ethereum can be ‘invested’ by permissioned actors to generate yield. In the case of USDS / sUSDS (Spark protocol), the yield is handed down to sUSDS users on Gnosis Chain. The addition of Hashi (EVM Hash Oracle Aggregator) and light clients for message validation is being tested but remains optional for now.
Incoming transfers are externally verified
Incoming messages to Ethereum are validated by Multisigs with publicly known entities as their signers. The DAI bridge validators are validated by the 4/7 BridgeValidators_DAI Multisig and the Omni bridge by the 4/7 BridgeValidators_Omni Multisig. Only messages signed by at least the threshold amount of validators from the respective multisig are accepted for releasing funds from the escrow contract or for executing messages.
Users can be censored if validators decide to not pass selected messages between chains.
Funds can be stolen if validators sign a malicious message to mint or release tokens that they did not burn or lock on the other side.
Funds can be frozen if validators don't relay messages between chains.
Destination tokens
Users receive wrapped ERC677 tokens on Gnosis Chain. There’s a separate bridge for Dai.
Rehypothecation
User assets in the bridge escrow are not locked and can be moved by permissioned actors. This is usually done to generate yield, which can then be forwarded to the users.
Funds can be stolen if there's an exploit in external contracts that are used to invest user deposits.
Funds can be frozen if there are not enough tokens in the escrow to service withdrawals due to investing.

Ethereum
Roles:
Permissioned to sign crosschain messages, attesting to their validity.
Actors:
A Multisig with 8/15 threshold.
- Can upgrade with no delay
- DaiForeignBridge
- ForeignAMB
- ForeignOmnibridge
- BridgeValidators_DAI
- BridgeValidators_Omni
- Can interact with DaiForeignBridge
- change all critical configurations like fees, yield farming for escrowed funds, limits, validating contract references
- Can interact with ForeignAMB
- change external validation logic refered to by this contract (e.g. Hashi)
- Can interact with ForeignOmnibridge
- change all critical configurations like yield farming for escrowed funds and limits
- Can interact with BridgeValidators_DAI
- change the threshold and manage signers
- Can interact with BridgeValidators_Omni
- change the threshold and manage signers
A Multisig with 4/7 threshold. Custom Multisignature contract for Validators.
- A Validator - acting directly
A Multisig with 2/3 threshold. Member of Gnosis Bridge Multisig.
- Can upgrade with no delay
- HashiManager_Omni
- HashiManager_DAI
- Can interact with HashiManager_Omni
- change critical configurations of the Hashi protocol like the validation contract addresses
- Can interact with HashiManager_DAI
- change critical configurations of the Hashi protocol like the validation contract addresses
Gnosis Chain
Actors:
A Multisig with 8/15 threshold.
- Can upgrade with no delay
- HomeAMB
- BridgeValidators_Gnosis
- HomeOmnibridge
- Can interact with BridgeValidators_Gnosis
- change the threshold and manage signers
A Multisig with 2/3 threshold. Member of GnosisSafeL2.
- Can upgrade with no delay
- HashiManager_Gnosis
- Can interact with HashiManager_Gnosis
- change critical configurations of the Hashi protocol like the validation contract addresses
A Multisig with 3/12 threshold.
A Multisig with 4/7 threshold. Custom multisignature contract for Validator addresses.

Ethereum
Token bridge implementation and escrow for DAI-related tokens. Escrowed Dai can be invested in the Spark protocol for sDai.
Contract handling inbound messages for the Hashi protocol.
A hub contract for the Hashi protocol, an EVM Hash Oracle Aggregator.
- Roles:
- admin: Hashi Multisig
- owner: Hashi Multisig
A hub contract for the Hashi protocol, an EVM Hash Oracle Aggregator.
- Roles:
- admin: Hashi Multisig
- owner: Hashi Multisig
Contract handling outbound messages for the Hashi protocol.
Gnosis Chain
Contract handling inbound messages for the Hashi protocol.
A hub contract for the Hashi protocol, an EVM Hash Oracle Aggregator.
- Roles:
- admin: GnosisSafeL2
- owner: GnosisSafeL2
- Roles:
- admin: GnosisSafeL2
Verifier contract for SP1 proofs (v5.0.0).
Contract handling outbound messages for the Hashi protocol.
- Roles:
- admin: GnosisSafeL2
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on code upgrades (CRITICAL).
