Search
Search for projects by name or address
 Cartesi PRT Honeypot
Cartesi PRT Honeypot
The chain deployment is permanently frozen after the team managed to find a bug in the PRT contracts.Read more
Badges
About
Cartesi PRT Honeypot is an application-specific Stage-2 rollup that stress-tests Cartesi Rollups’ security. Protected solely by Cartesi’s PRT (Permissionless Refereed Tournaments) fraud-proof algorithm, it turns its locked funds into an open bounty for... anyone who can break the system. Users should not deposit unless they are willing to donate their funds to the Honeypot.
Badges
About
Cartesi PRT Honeypot is an application-specific Stage-2 rollup that stress-tests Cartesi Rollups’ security. Protected solely by Cartesi’s PRT (Permissionless Refereed Tournaments) fraud-proof algorithm, it turns its locked funds into an open bounty for... anyone who can break the system. Users should not deposit unless they are willing to donate their funds to the Honeypot.
The section shows the operating costs that L2s pay to Ethereum.
2025 Jun 11 — 2026 Feb 21
This section shows how "live" the project's operators are by displaying how frequently they submit transactions of the selected type. It also highlights anomalies - significant deviations from their typical schedule.
2025 Jun 11 — 2026 Feb 22
Cartesi PRT Honeypot reached a fail-stop state
2025 Sep 24th
The chain is permanently frozen after the team managed to find a bug in the PRT contracts.
Fraud proofs allow actors watching the chain to prove that the state is incorrect. Interactive proofs (INT) require multiple transactions over time to resolve.
All of the data needed for proof construction is published on Ethereum L1.
Users cannot exit their funds as all deposits are considered donations.
Rollup operators cannot compromise the system, but being application-specific might bring additional risk.
Users can deposit (donate) CTSI tokens to the Honeypot. The funds can only be withdrawn by the Cartesi Multisig to its own address. The appchain has the very specific purpose of a bug bounty on the proof system, incentivizing security researchers to break it and claim the deposited funds.
The genesis state comes from the Honeypot Cartesi Machine template included in the Honeypot v2 release. Alternatively, you can recreate it by following the build steps in the Honeypot GitHub Repository.
The information in the section might be incomplete or outdated.
The L2BEAT Team is working to research & validate the content before publishing.
After some period of time, the published state root is assumed to be correct. For a certain time period, usually one week, anyone can submit a fraud proof that shows that the state was incorrect.
Funds can be stolen if there is no one that checks the published state. Fraud proofs assume at least one honest and able validator.
There is no central operator
There is no privileged entity that sequences transactions or produces blocks. This activity is permissionless and open to anyone.
Users can force any transaction
Because the state of the system is based on transactions submitted on the underlying host chain and anyone can submit their transactions there it allows the users to circumvent censorship by interacting with the smart contract on the host chain directly.
No user withdrawals
No address apart from the Cartesi Multisig can trigger a withdrawal and deposits are considered donations to the Honeypot. If a withdrawal is requested by them, all funds in the escrow are withdrawable to the permissioned address as soon as the next settlement on L1 occurs (min. every 7d 1h).

Ethereum
Actors:
A Multisig with 3/6 threshold.
- Can interact with Application
- withdraw the entire balance in the escrow

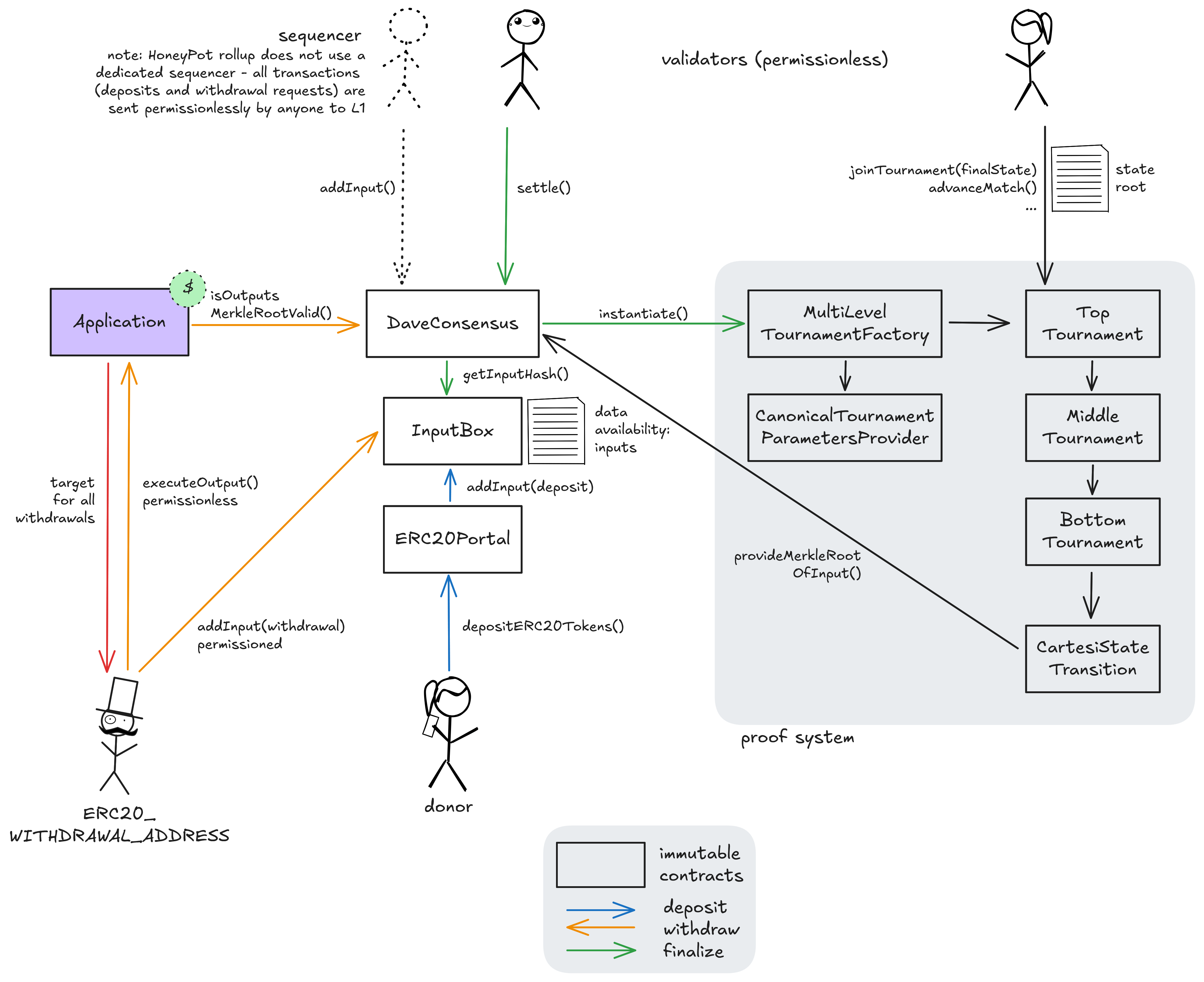
Ethereum
Main dApp contract that escrows assets and executes the verified results (outputs) from off-chain computation. It relies on the DaveConsensus contract to validate outputs before releasing assets or triggering on-chain actions. The immutable template hash of the dApp is 0x615acc9fb8ae058d0e45c0d12fa10e1a6c9e645222c6fd94dfeda194ee427c14.
- Roles:
- withdrawer: Cartesi Multisig
- This contract can store any token.
Contract managing PRT fraud-proof tournaments, application epochs and input validation, as well as settlement and challenge periods. Dispute tournaments are started here and the final, verified computation result (as an outputsMerkleRoot) is recorded when they are resolved.
Serves as both the canonical log for arbitrary dApp inputs and a portal for depositing assets (one possible type of input). It ensures data availability and that all off-chain participants process the same inputs in the same order.
Represents the entry point and highest level of a dispute in PRT. Disagreeing validators join this tournament to resolve conflicts over the entire computation trace through a bisection game.
Referees the dispute over a single contested Cartesi machine step as the final stage of arbitration in a dispute. It calls the CartesiStateTransition contract to get a definitive on-chain ruling and identify the winner.
Onchain verifier that can execute a single, disputed instruction of the Cartesi machine. It is the ultimate arbiter that BottomTournament calls to determine which party’s claimed state transition is correct.
Responsible for creating and orchestrating the multi-stage dispute process. It instantiates the correct tournament contract (Top, Middle, or Bottom) depending on the current stage of the dispute game.
Contract that allows anyone to perform transfers of ERC-20 tokens to Cartesi DApps.
Provides constant configuration data for the tournament system. It defines parameters like the number of levels (3), the minimum challenge period of ~7d, and the size of computation segments at each stage of a dispute.
Handles the intermediate stages of a dispute following the TopTournament targeting a more granular bisection game.
Value Secured is calculated based on these smart contracts and tokens:
Contract storing bounty funds.
