Search
Search for projects by name or address
 Fuel Ignition
Fuel Ignition
Badges
About
Fuel Ignition is a high-performance Ethereum L2 built on FuelVM and the Sway language.
Badges
About
Fuel Ignition is a high-performance Ethereum L2 built on FuelVM and the Sway language.
Why is the project listed in others?
Consequence: projects without a proper proof system fully rely on single entities to safely update the state. A malicious proposer can finalize an invalid state, which can cause loss of funds.
Consequence: projects without a data availability bridge fully rely on single entities (the sequencer) to honestly rely available data roots on Ethereum. A malicious sequencer can collude with the proposer to finalize an unavailable state, which can cause loss of funds.
Learn more about the recategorisation here.
2025 Mar 04 — 2026 Mar 03
The section shows the operating costs that L2s pay to Ethereum.
2025 Mar 04 — 2026 Mar 04
This section shows how much data the project publishes to its data-availability (DA) layer over time. The project currently posts data to![]() EigenDA; previously it posted to
EigenDA; previously it posted to![]() Ethereum.
Ethereum.
2025 Mar 04 — 2026 Mar 03
This section shows how "live" the project's operators are by displaying how frequently they submit transactions of the selected type. It also highlights anomalies - significant deviations from their typical schedule.
Funds can be stolen if
Funds can be lost if
Funds can be frozen if
MEV can be extracted if
Currently the system permits invalid state roots. More details in project overview.
There is no window for users to exit in case of an unwanted regular upgrade since contracts are instantly upgradable.
Only the whitelisted proposers can publish state roots on L1, so in the event of failure the withdrawals are frozen.
Data is posted to EigenDA
No transactions roots are posted onchain and the full data is posted on EigenDA. Since the ServiceManager bridge is not used, availability of the data is not verified against EigenDA operators, meaning that data is not guaranteed to be available.
Funds can be lost if the data is not available on the external provider (CRITICAL).
Ultimately, Fuel will use one round fraud proofs with single round performed via a RISC-V-based zkVM. Currently, there is a 1d challenge period.
Funds can be stolen if an invalid state root is submitted to the system by the proposer (CRITICAL).
The system has a centralized sequencer
While forcing transaction is open to anyone the system employs a privileged sequencer that has priority for submitting transaction batches and ordering transactions.
MEV can be extracted if the operator exploits their centralized position and frontruns user transactions.
Users can force any transaction
Because the state of the system is based on transactions submitted on the underlying host chain and anyone can submit their transactions there it allows the users to circumvent censorship by interacting with the smart contract on the host chain directly.
Forced messaging
If the user experiences censorship from the operator with regular L2->L1 messaging they can submit their messages directly on L1. The system is then obliged to service this request or halt all messages, including forced withdrawals from L1 and regular messages initiated on L2. Once the force operation is submitted and if the request is serviced, the operation follows the flow of a regular message.
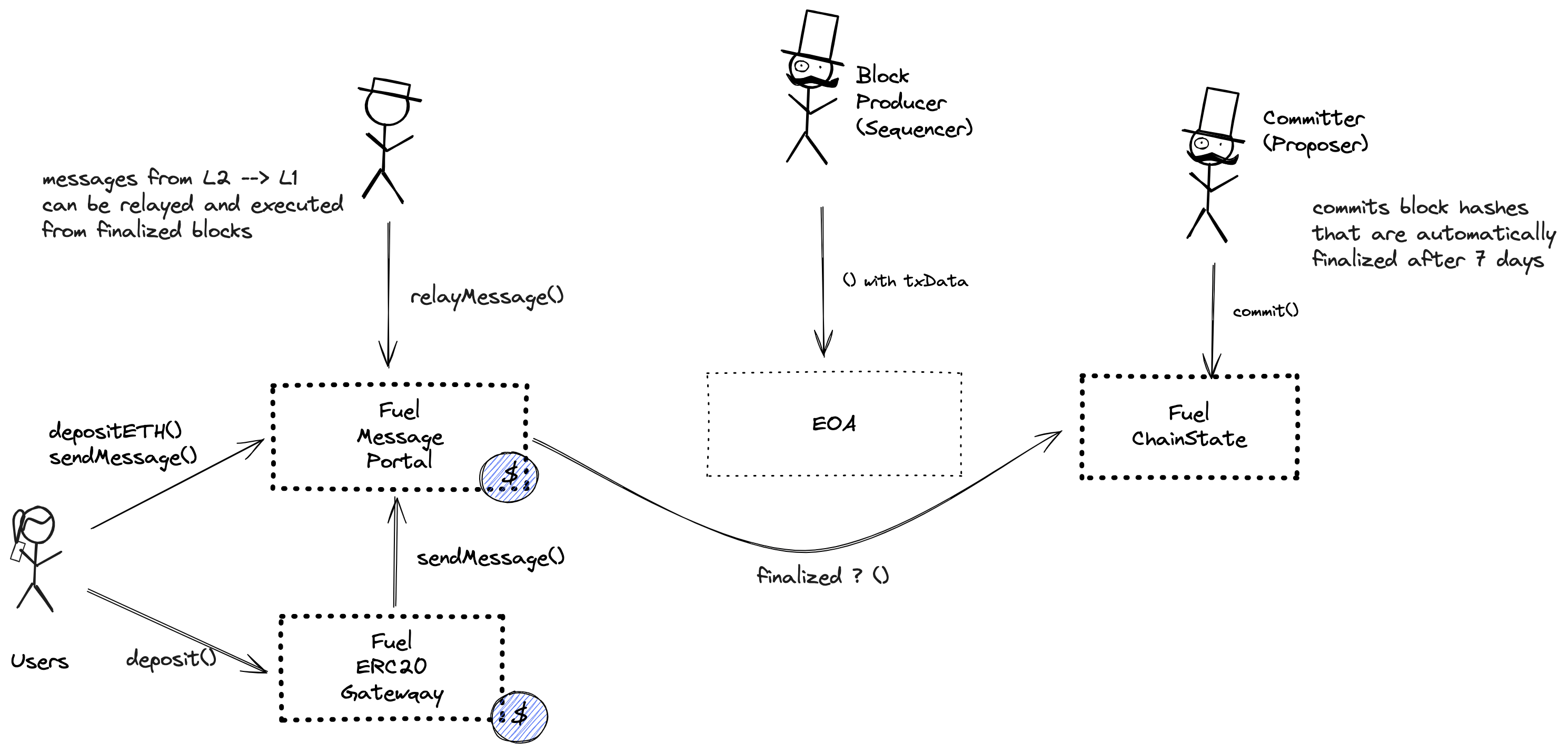
Fuel operates via the FuelVM and the Sway language
The FuelVM makes use of the UTXO model and a register-based design to enable parallel transaction processing. The language used is Sway and it does not support Solidity contracts.

Ethereum
Actors:
Whitelisted addresses that can pause the ERC20Gateway.
Whitelisted addresses that can pause the FuelChainState.
Permissioned address that can propose new state roots.

Ethereum
Standard gateway to deposit and withdraw ERC20 tokens. It implements rate limits and a whitelist for tokens. The whitelist is currently active.
- This contract can store any token.
Contract that allows state root submissions and settlement.
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on upgrades (CRITICAL).
Funds can be frozen if pausers blacklist L2->L1 messages (CRITICAL).
Funds can be frozen if the limit of tokens that can be withdrawn is set too low.
