Search
Search for projects by name or address
 Scroll
Scroll
Badges
About
Scroll is ZK Rollup that extends Ethereum’s capabilities through ZK tech and EVM compatibility.
Badges
About
Scroll is ZK Rollup that extends Ethereum’s capabilities through ZK tech and EVM compatibility.
2025 Mar 04 — 2026 Mar 04
The section shows the operating costs that L2s pay to Ethereum.
2025 Mar 04 — 2026 Mar 04
This section shows how much data the project publishes to its data-availability (DA) layer over time. The project currently posts data to![]() Ethereum.
Ethereum.
2025 Mar 04 — 2026 Mar 04
This section shows how "live" the project's operators are by displaying how frequently they submit transactions of the selected type. It also highlights anomalies - significant deviations from their typical schedule.
Funds can be stolen if
MEV can be extracted if
STARKs and SNARKs are zero knowledge proofs that ensure state correctness. STARKs proofs are wrapped in SNARKs proofs for efficiency. SNARKs require a trusted setup.
All of the data needed for proof construction is published on Ethereum L1.
There is no window for users to exit in case of an unwanted regular upgrade since contracts are instantly upgradable.
All data required for proofs is published on chain
All the data that is used to construct the system state is published on chain in the form of cheap blobs or calldata. This ensures that it will be available for enough time.
Each update to the system state must be accompanied by a ZK proof that ensures that the new state was derived by correctly applying a series of valid user transactions to the previous state. These proofs are then verified on Ethereum by a smart contract.
SNARK verification keys can be generated and checked against Ethereum verifier contract using this guide. The system requires a trusted setup.
Each update to the system state must be accompanied by a ZK proof that ensures that the new state was derived by correctly applying a series of valid user transactions to the previous state. These proofs are then verified on Ethereum by a smart contract.
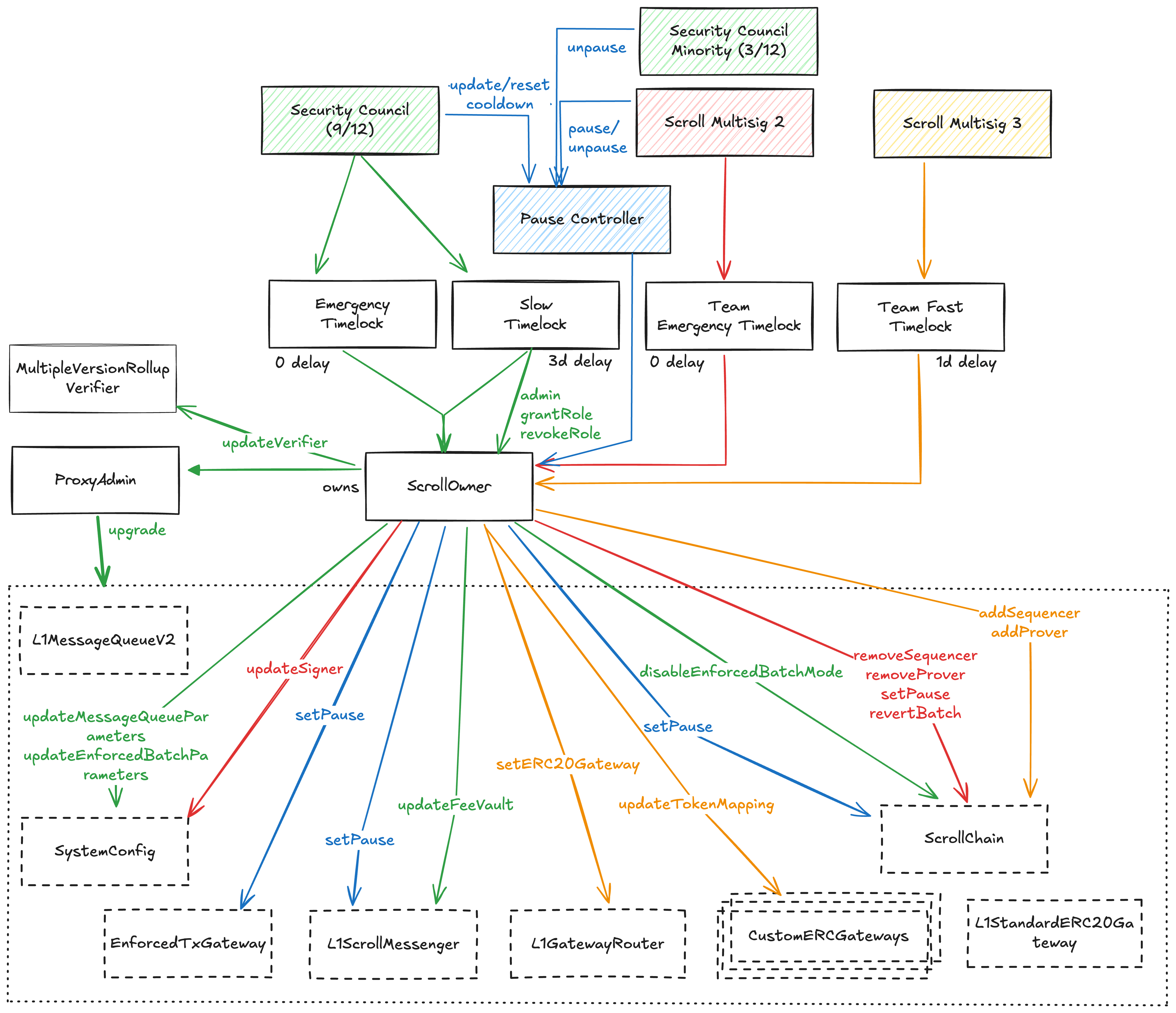
All core contracts in the Scroll protocol are upgradable by the ProxyAdmin, which is controlled by the Security Council through the ScrollOwner contract. The ScrollOwner is a central governance contract controlled by four distinct Timelocks: two governed by the Security Council multisig and two by the Scroll team multisigs. Each multisig can initiate specific types of changes with differing delay guarantees. The team has authority to revert unfinalized batches and add or remove sequencers and provers while sequencing is in permissioned mode. As the ScrollOwner admin, the Security Council can revert the team actions by revoking the team roles in the ScrollOwner contract (through the TimelockSCSlow) and upgrading the affected contracts. The Security Council can change parameters that affect L1->L2 messaging and the activation of permissionless sequencing (i.e., enforcedBatchMode), such as by calling the updateMessageQueueParameters and updateEnforcedBatchParameters functions or by pausing the EnforcedTXGateway. Emergency pause of core contracts is managed through the PauseController, which allows the team to pause batch commitment and finalization in permissioned mode, as well as L1->L2 messaging. Each pause is subject to a cooldown period of 1mo execution delay, during which the Security Council minority can unpause, while the Security Council majority is authorized to update and reset the cooldown period. SCR token holders perform onchain voting on governance proposals through the AgoraGovernor contract on L2. However, onchain governance proposals do not contain transaction payloads, so onchain voting only acts as an onchain temperature check. The Security Council is in charge of executing upgrades.
The system has a centralized sequencer
While forcing transaction is open to anyone the system employs a privileged sequencer that has priority for submitting transaction batches and ordering transactions.
MEV can be extracted if the operator exploits their centralized position and frontruns user transactions.
Users can force any transaction
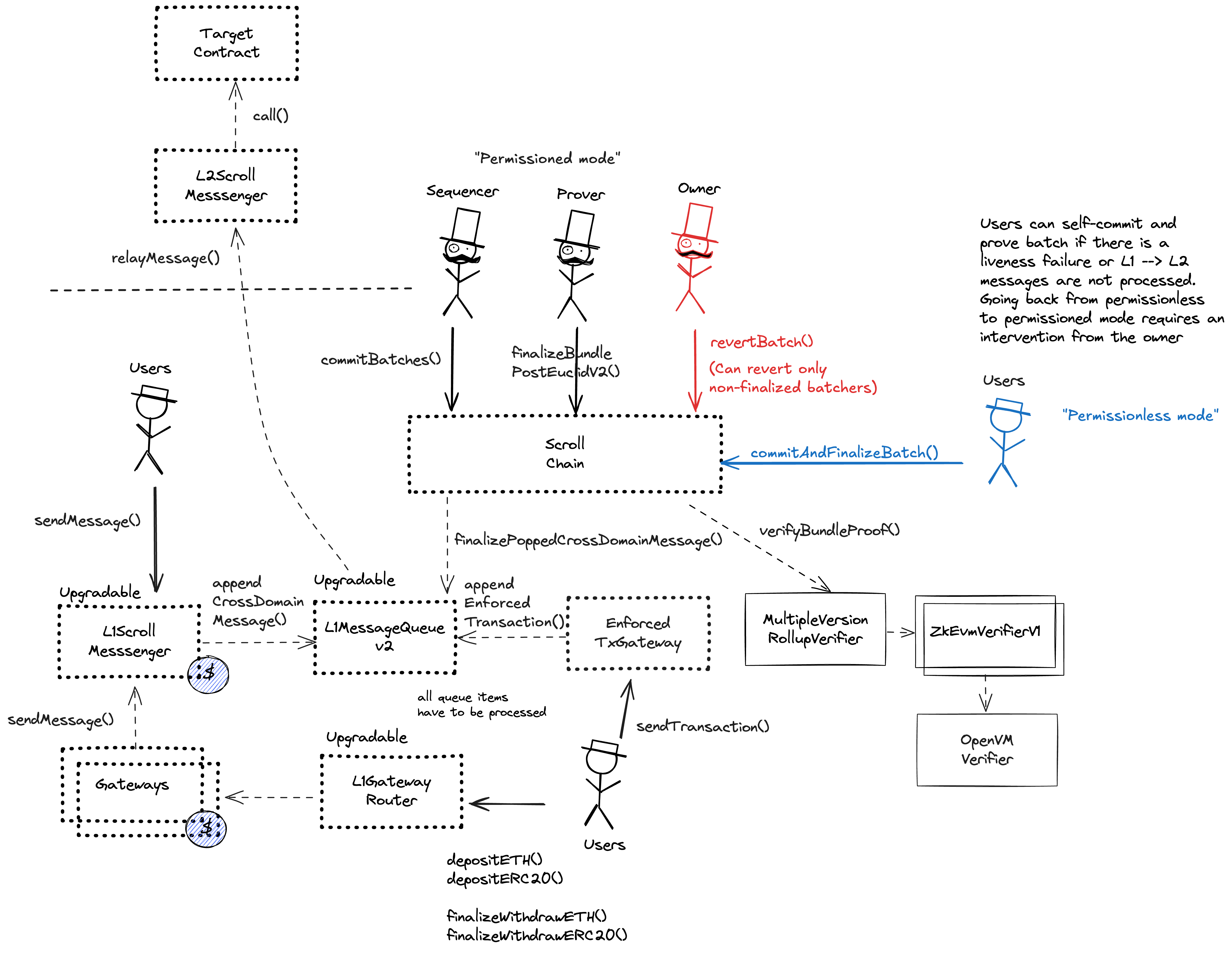
Because the state of the system is based on transactions submitted on the underlying host chain and anyone can submit their transactions there it allows the users to circumvent censorship by interacting with the smart contract on the host chain directly. The enforced liveness mechanism is activated if either an L1 message has not been finalized for more than 7d or a batch has not been finalized for more than 7d. When activated, transactions that were directly posted to the smart contract can be forcefully included by anyone on the host chain, which finalizes their ordering.

Ethereum
Actors:
A Multisig with 9/12 threshold.
- Can interact with TimelockSCEmergency
- cancel queued transactions
- execute transactions that are ready
- propose transactions
- update the minimum delay and manage all access control roles of the timelock TimelockSCEmergency - or - acting directly
- Can interact with TimelockSCSlow
- cancel queued transactions
- execute transactions that are ready
- propose transactions
- update the minimum delay and manage all access control roles of the timelock with 3d delay or with no delay TimelockSCSlow with 3d delay - or - acting directly
- Can interact with ScrollOwner
- disable enforced batch mode TimelockSCEmergency
- update and reset the PauseController cooldown period TimelockSCEmergency
- update ScrollChain zk proof verifier TimelockSCEmergency
- update the L1ScrollMessenger fee vault address TimelockSCEmergency
- update the minimum delay message queue parameters and enforced mode parameters TimelockSCEmergency
- upgrade all core contracts of the system TimelockSCEmergency
A Multisig with 2/4 threshold.
- Can interact with ScrollOwner
- Can interact with TimelockEmergency
- cancel queued transactions
- propose transactions
- update the minimum delay and manage all access control roles of the timelock TimelockEmergency - or - acting directly
A Multisig with 3/5 threshold.
- Can interact with TimelockFast
- cancel queued transactions
- propose transactions
- update the minimum delay and manage all access control roles of the timelock with 1d delay or with no delay TimelockFast with 1d delay - or - acting directly
- Can interact with ScrollOwner
- add permissioned batchers and provers to the whitelist with 1d delay TimelockFast with 1d delay
- set ERC20 gateways in the L1GatewayRouter with 1d delay TimelockFast with 1d delay
A Multisig with 3/12 threshold.
- Can interact with ScrollOwner
- unpause core contracts via the PauseController
Manager contract for minter management [sic].
- Can interact with Euro Coin Token
- manage minter addresses
Member of Scroll Multisig 1, Scroll Multisig 4, Scroll Multisig 2.
- Can interact with TimelockSCEmergency
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockFast
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockSCSlow
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockEmergency
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
Member of Scroll Multisig 1, Scroll Multisig 4, Scroll Multisig 2, Scroll Multisig 3.
- Can interact with TimelockSCEmergency
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockFast
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockSCSlow
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockEmergency
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
Member of Scroll Multisig 1, Scroll Multisig 2, Scroll Multisig 3.
- Can interact with TimelockSCEmergency
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockFast
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockSCSlow
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockEmergency
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with Euro Coin Token
- pause the USDC token (no transfers, mints, burns)
- Can interact with Euro Coin Token
- manage all critical roles like pausers, blacklisters, minters, rescuer
- Can interact with Euro Coin Token
- blacklist addresses, freezing any interactions with the USDC token for them
- Can upgrade with no delay
- Euro Coin Token
Scroll
Actors:
A Multisig with 9/12 threshold.
- Can interact with ScrollOwner
- disable enforced batch mode TimelockSCEmergencyScroll
- update ScrollChain zk proof verifier TimelockSCEmergencyScroll
- upgrade all core contracts of the system TimelockSCEmergencyScroll
- Can interact with TimelockSCEmergencyScroll
- cancel queued transactions
- execute transactions that are ready
- propose transactions
- update the minimum delay and manage all access control roles of the timelock TimelockSCEmergencyScroll - or - acting directly
- Can interact with AgoraGovernor
- can configure contract settings such as voting delay, quorum, contract manager with 3d delay TimelockSCSlow with 3d delay
A Multisig with 2/4 threshold.
- Can interact with TimelockEmergency
- cancel queued transactions
- propose transactions
- update the minimum delay and manage all access control roles of the timelock TimelockEmergency - or - acting directly
A Multisig with 3/5 threshold.
- Can interact with TimelockFast
- cancel queued transactions
- propose transactions
- update the minimum delay and manage all access control roles of the timelock with 1d delay or with no delay TimelockFast with 1d delay - or - acting directly
A Multisig with 2/2 threshold.
- Can interact with AgoraGovernor
- can propose new onchain governance proposals without the required threshold of votes
- Can upgrade with no delay
- L2LidoGateway
A Multisig with 3/12 threshold.
Member of Scroll Multisig 1, Scroll Multisig 2.
- Can interact with TimelockSCEmergencyScroll
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockFast
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockEmergency
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
Member of Scroll Multisig 1, Scroll Multisig 2, Scroll Multisig 3.
- Can interact with TimelockSCEmergencyScroll
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockFast
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1
- Can interact with TimelockEmergency
- execute transactions that are ready Scroll Multisig 1

Ethereum
Contract used to update the verifier and keep track of current and old versions.
Contract used to send L1 -> L2 and relay messages from L2. It allows to replay failed messages and to drop skipped messages. L1 -> L2 messages sent using this contract pay for L2 gas on L1 and will have the aliased address of this contract as the sender.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
- This contract stores the following tokens: ETH.
Owner of all contracts in the system. It implements an extension of AccessControl that manages roles and functions allowed to be called by each role.
- Roles:
- opsFast: TimelockFast; ultimately Scroll Multisig 3
- opsNoDelay: TimelockEmergency; ultimately Scroll Multisig 2
- scMinorityNoDelay: Scroll Security Council Minority
- scNoDelay: TimelockSCEmergency; ultimately Scroll Security Council
System configuration contract for Scroll, contains enforcedBatchParameters and messageQueueParameters determining permissionless mode.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
- owner: ScrollOwner
The main contract of the Scroll chain. Allows to post transaction data and state roots, along with proofs. Sequencing and proposing are behind a whitelist unless enforcedBatchMode is activated.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
A timelock with access control. The current minimum delay is 0s. Proposals that passed their minimum delay can be executed by the anyone.
- Roles:
- canceller: Scroll Security Council
- executor: Scroll Multisig 1, Scroll Security Council; ultimately EOA 1, EOA 2, EOA 3, EOA 4
- proposer: Scroll Security Council
- timelockAdmin: Scroll Security Council, TimelockSCEmergency; ultimately Scroll Security Council
A timelock with access control. The current minimum delay is 1d. Proposals that passed their minimum delay can be executed by the anyone.
- Roles:
- canceller: Scroll Multisig 3
- executor: Scroll Multisig 1; ultimately EOA 1, EOA 2, EOA 3, EOA 4
- proposer: Scroll Multisig 3
- timelockAdmin: Scroll Multisig 3, TimelockFast; ultimately Scroll Multisig 3
A timelock with access control. The current minimum delay is 3d. Proposals that passed their minimum delay can be executed by the anyone.
- Roles:
- canceller: Scroll Security Council
- executor: Scroll Multisig 1, Scroll Security Council; ultimately EOA 1, EOA 2, EOA 3, EOA 4
- proposer: Scroll Security Council
- timelockAdmin: Scroll Security Council, TimelockSCSlow; ultimately Scroll Security Council
A timelock with access control. The current minimum delay is 0s. Proposals that passed their minimum delay can be executed by the anyone.
- Roles:
- canceller: Scroll Multisig 2
- executor: Scroll Multisig 1; ultimately EOA 1, EOA 2, EOA 3, EOA 4
- proposer: Scroll Multisig 2
- timelockAdmin: Scroll Multisig 2, TimelockEmergency; ultimately Scroll Multisig 2
Main entry point for depositing ETH and ERC20 tokens, which are then forwarded to the correct gateway.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
This contract stores the following tokens: wstETH.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
- This contract stores the following tokens: DAI.
- Roles:
- admin: EOA 12
- blacklister: EOA 11
- masterMinter: MasterMinter
- owner: EOA 10
- pauser: EOA 9
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
- Roles:
- owner: ScrollOwner
Scroll
Owner of all contracts in the system. It implements an extension of AccessControl that manages roles and functions allowed to be called by each role.
- Roles:
- scNoDelay: TimelockSCEmergencyScroll; ultimately Scroll Security Council
A timelock with access control. The current minimum delay is 0s. Proposals that passed their minimum delay can be executed by the anyone.
- Roles:
- canceller: Scroll Security Council
- executor: Scroll Multisig 1, Scroll Security Council; ultimately EOA 5, EOA 6, EOA 7, EOA 8
- proposer: Scroll Security Council
- timelockAdmin: Scroll Security Council, TimelockSCEmergencyScroll; ultimately Scroll Security Council
A timelock with access control. The current minimum delay is 1d. Proposals that passed their minimum delay can be executed by the anyone.
- Roles:
- canceller: Scroll Multisig 3
- executor: Scroll Multisig 1; ultimately EOA 5, EOA 6, EOA 7, EOA 8
- proposer: Scroll Multisig 3
- timelockAdmin: Scroll Multisig 3, TimelockFast; ultimately Scroll Multisig 3
Used to propose and manage onchain governance proposals.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
- manager: GnosisSafeL2
- timelock: TimelockSCSlow; ultimately Scroll Security Council
A timelock with access control. The current minimum delay is 0s. Proposals that passed their minimum delay can be executed by the anyone.
- Roles:
- canceller: Scroll Multisig 2
- executor: Scroll Multisig 1; ultimately EOA 5, EOA 6, EOA 7, EOA 8
- proposer: Scroll Multisig 2
- timelockAdmin: Scroll Multisig 2, TimelockEmergency; ultimately Scroll Multisig 2
Contract of the USDC token on Scroll.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
Counterpart to the L1GatewayRouter contract.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
Used to append messages to the L2MessageQueue from the L2ScrollMessenger.
Counterpart to the L1ERC1155Gateway contract.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
Counterpart to the L1CustomERC20Gateway contract.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
Contract used to deploy ScrollStandardERC20 tokens for L2StandardERC20Gateway.
Contract of the L2ScrollMessenger contract.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
ETH is pre-minted to this contract in the genesis block and released on Scroll whenever corresponding deposits are made on Ethereum.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
- Roles:
- timelockAdmin: Scroll Security Council, TimelockSCSlow
Counterpart to the L1ERC721Gateway contract.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
- Roles:
- owner: ScrollOwner
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
- Roles:
- owner: ScrollOwner
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
Contract that uses controllers to manage minters for USDC on Scroll.
Contract of the ERC20 standard token used by the ERC20 factory.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin
- Roles:
- owner: ScrollOwner
Value Secured is calculated based on these smart contracts and tokens:
Custom token escrow governed by Lido, using the canonical bridge for messaging.
Custom token escrow governed by puffer.fi, using the canonical bridge for messaging.
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on code upgrades (CRITICAL).
