Search
Search for projects by name or address
 zkLink Nova
zkLink Nova
Badges
About
zkLink Nova is a Layer 3 zkEVM Validium network leveraging ZK Stack that allows for scattered assets across Ethereum Layer 2s to be aggregated for interoperable trade and transactions.
Badges
About
zkLink Nova is a Layer 3 zkEVM Validium network leveraging ZK Stack that allows for scattered assets across Ethereum Layer 2s to be aggregated for interoperable trade and transactions.
Why is the project listed in others?
Consequence: projects without a data availability bridge fully rely on single entities (the sequencer) to honestly rely available data roots on Ethereum. A malicious sequencer can collude with the proposer to finalize an unavailable state, which can cause loss of funds.
Learn more about the recategorisation here.
2025 Feb 28 — 2026 Feb 28
Funds can be stolen if
Funds can be lost if
Users can be censored if
MEV can be extracted if
| SEQUENCER FAILURE | STATE VALIDATION | DATA AVAILABILITY | EXIT WINDOW | PROPOSER FAILURE | |
| Linea L2 | No mechanism | Validity proofs (SN) | Onchain | None | Cannot withdraw |
| zkLink Nova L3 • Individual | Enqueue via L2 | Validity proofs (ST, SN) | External | None | Cannot withdraw |
| zkLink Nova L3 • Combined | No mechanism | Validity proofs | External | None | Cannot withdraw |
There is no mechanism to have transactions be included if the sequencer is down or censoring.
Zero knowledge cryptography is used to ensure state correctness. Proofs are first verified on Linea and finally on Ethereum.
Proof construction and state derivation rely fully on data that is ultimately NOT published on Ethereum.
There is no window for users to exit in case of an unwanted regular upgrade since contracts are instantly upgradable.
Only the whitelisted proposers can publish state roots on L1, so in the event of failure the withdrawals are frozen.
Data is not stored on chain
The transaction data is not recorded on the Ethereum main chain.
Funds can be lost if the external data becomes unavailable (CRITICAL).
The system has a centralized operator
The validators are the only entities that can propose blocks and process transactions. Moreover, they are trusted to only relay valid messages using the fast path. Fast path messages are eventually checked against the slow path, and if they are invalid, the system halts.
MEV can be extracted if the operator exploits their centralized position and frontruns user transactions.
Funds can be lost if the operator relays invalid messages using the fast path (CRITICAL).
Users can force any transaction via L2
Users can be censored if the operator refuses to include their transactions.
Forced messaging
If the user experiences censorship from the operator with regular L2->L1 messaging they can submit their messages directly on L1. The system is then obliged to service this request or halt all messages from L1, including all forced withdrawals and deposits. Once the force operation is submitted and if the request is serviced, the operation follows the flow of a regular message.
Bridging from multiple chains
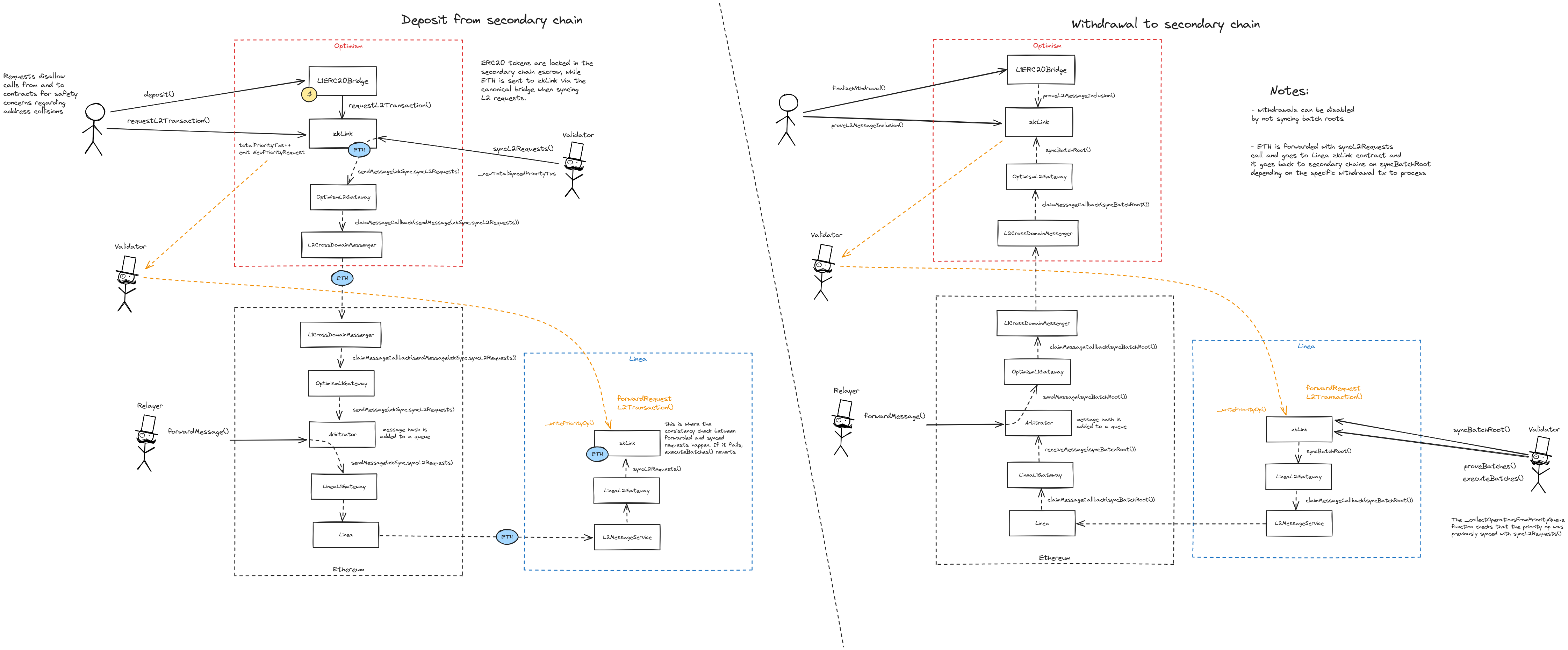
zkLink allows users to bridge assets from multiple chains, not just the base chain Linea. To do this, messages are sent through the canonical bridges of each respective chain to the main zkLink contract on Linea. To withdraw, state updates are relayed back to each chain with the respective canonical bridges. Since deposits in this way are processed quite slowly, the system allows validators to relay messages directly to the main zkLink contract in a trusted way. These messages are then checked against the slow path, and if they are invalid, the system eventually halts.
Funds can be lost if the canonical bridges of the secondary chains are compromised.

Linea
Actors:
A Multisig with 5/8 threshold. Admin of the main zkLink contract, meaning it can upgrade the bridge implementation and potentially gain access to all funds.
Permissioned actors that can commit, prove and execute blocks. It can also “fast” relay messages to zkLink Nova without going through the canonical bridges, meaning it can potentially relay invalid messages and mint tokens out of thin air. In that case, since the system checks such messages against the slow path, after some time the system would halt.
OP Mainnet
Actors:
Owner of the L1ERC20Bridge on OP Mainnet.
A Multisig with 5/8 threshold. Admin of the zkLink contract on OP Mainnet and the ProxyAdmin, meaning it can upgrade the bridge implementation and potentially gain access to all funds.
Arbitrum One
Actors:
Owner of the L1ERC20Bridge on Arbitrum One.
A Multisig with 5/8 threshold. Admin of the zkLink contract on Arbitrum One and the ProxyAdmin, meaning it can upgrade the bridge implementation and potentially gain access to all funds.
Base Chain
Actors:
Owner of the L1ERC20Bridge on Base.
A Multisig with 5/8 threshold. Admin of the zkLink contract on Base and the ProxyAdmin, meaning it can upgrade the bridge implementation and potentially gain access to all funds.
Manta Pacific
Actors:
Owner of the L1ERC20Bridge on Manta Pacific.
Admin of the zkLink contract on Manta Pacific and the ProxyAdmin, meaning it can upgrade the bridge implementation and potentially gaining access to all funds.
Mantle
Actors:
Owner of the L1ERC20Bridge on Mantle.
A Multisig with 5/8 threshold. Admin of the zkLink contract on Mantle and the ProxyAdmin, meaning it can upgrade the bridge implementation and potentially gain access to all funds.
Scroll
Actors:
Owner of the L1ERC20Bridge on Scroll.
A Multisig with 5/7 threshold. Admin of the zkLink contract on Scroll and the ProxyAdmin, meaning it can upgrade the bridge implementation and potentially gain access to all funds.
Blast
Actors:
Owner of the L1ERC20Bridge on Blast.
A Multisig with 6/8 threshold. Admin of the zkLink contract on Blast and the ProxyAdmin, meaning it can upgrade the bridge implementation and potentially gain access to all funds.
ZKsync Era
Actors:
Owner of the L1ERC20Bridge on ZKsync Era.
A Multisig with 5/8 threshold. Admin of the zkLink contract on ZKsync Era and the ProxyAdmin, meaning it can upgrade the bridge implementation and potentially gain access to all funds.
Ethereum
Actors:
Owner of the L1ERC20Bridge on Ethereum.
A Multisig with 5/8 threshold. Admin of the zkLink contract on Ethereum and the ProxyAdmin, meaning it can upgrade the bridge implementation and potentially gain access to all funds.

Linea
Main entry point for depositing ERC20 tokens from Linea to zkLink Nova. Outgoing messages and incoming withdrawal validation is delegated to the zkLink contract.
- This contract can store any token.
Main contract of the system where blocks are committed, proven and executed. It syncs messages from secondary chains (“slow” path) and accepts “fast” forwarded requests from permissioned validators that are later cross-checked with the slow path. ETH coming from secondary chains are transferred and escrowed here. State roots are then synced back to the secondary chains. The source code of this contract is not verified on Etherscan.
- This contract stores the following tokens: ETH.
High level interface between the main zkLink contract and Linea’s message service.
Intermediary contract between the one of the validators and the ZKsync Era diamond that can delay block execution (ie withdrawals and other L3 --> L2 messages). Currently, the delay is set to 0s.
Intermediary governance contract with two roles and a customizable delay. This delay is only mandatory for transactions scheduled by the Owner role and can be set by the SecurityCouncil role. The SecurityCouncil role can execute arbitrary upgrade transactions immediately. Currently the delay is set to 0s and the SecurityCouncil role is not used.
Ethereum
Main entry point for depositing ERC20 tokens from Ethereum to zkLink Nova. Outgoing messages and incoming withdrawal validation is delegated to the zkLink contract.
- This contract can store any token.
Main messaging contract on Ethereum and ETH escrow. Outgoing messages (like deposits) are sent through the EthereumL2Gateway which ultimately makes use of Ethereum’s canonical messaging bridge to reach the Arbitrator on L1. Only whitelisted validators can sync messages with zkLink Nova, which also transfer the ETH to it via the respective canonical bridges. Incoming messages (like withdrawals) are validated on Linea first and then sent to this contract through the same path. Whitelisted validators can also relay messages to zkLink without going through the canonical bridge (fast path), which are later cross-checked with the slow path. If the check fails, the system halts.
- This contract stores the following tokens: ETH.
High level interface between the local zkLink contract and Ethereum’s message service.
Contract storing the mapping between secondary chain bridges and acts as an intermediary to receive and relay messages to and from the main zkLink contract.
L1 counterpart receiving messages from the LineaL2Gateway on Linea. It redirects them to the Arbitrator contract.
L1 counterpart receiving messages from the MantaL2Gateway on Manta Pacific. It redirects them to the Arbitrator contract.
L1 counterpart receiving messages from the MantleL2Gateway on Mantle. It redirects them to the Arbitrator contract.
L1 counterpart receiving messages from the EraL2Gateway on ZKsync Era. It redirects them to the Arbitrator contract.
L1 counterpart receiving messages from the ArbitrumL2Gateway on Arbitrum One. It redirects them to the Arbitrator contract.
L1 counterpart receiving messages from the BlastL2Gateway on Blast. It redirects them to the Arbitrator contract.
L1 counterpart receiving messages from the OptimismL2Gateway on OP Mainnet. It redirects them to the Arbitrator contract.
L1 counterpart receiving messages from the BaseL2Gateway on Base. It redirects them to the Arbitrator contract.
L1 counterpart receiving messages from the ScrollL2Gateway on Scroll. It redirects them to the Arbitrator contract.
OP Mainnet
Main entry point for depositing ERC20 tokens from OP Mainnet to zkLink Nova. Outgoing messages and incoming withdrawal validation is delegated to the zkLink contract.
- This contract can store any token.
Main messaging contract on OP Mainnet and ETH escrow. Outgoing messages (like deposits) are sent through the OptimismL2Gateway which ultimately makes use of OP Mainnet’s canonical messaging bridge to reach the Arbitrator on L1. Only whitelisted validators can sync messages with zkLink Nova, which also transfer the ETH to it via the respective canonical bridges. Incoming messages (like withdrawals) are validated on Linea first and then sent to this contract through the same path. Whitelisted validators can also relay messages to zkLink without going through the canonical bridge (fast path), which are later cross-checked with the slow path. If the check fails, the system halts.
- This contract stores the following tokens: ETH.
High level interface between the local zkLink contract and OP’s message service.
Arbitrum One
Main entry point for depositing ERC20 tokens from Arbitrum One to zkLink Nova. Outgoing messages and incoming withdrawal validation is delegated to the zkLink contract.
- This contract can store any token.
Main messaging contract on Arbitrum One and ETH escrow. Outgoing messages (like deposits) are sent through the ArbitrumL2Gateway which ultimately makes use of Arbitrum One’s canonical messaging bridge to reach the Arbitrator on L1. Only whitelisted validators can sync messages with zkLink Nova, which also transfer the ETH to it via the respective canonical bridges. Incoming messages (like withdrawals) are validated on Linea first and then sent to this contract through the same path. Whitelisted validators can also relay messages to zkLink without going through the canonical bridge (fast path), which are later cross-checked with the slow path. If the check fails, the system halts.
- This contract stores the following tokens: ETH.
High level interface between the local zkLink contract and Arbitrum’s message service.
Base Chain
Main entry point for depositing ERC20 tokens from Base to zkLink Nova. Outgoing messages and incoming withdrawal validation is delegated to the zkLink contract.
- This contract can store any token.
Main messaging contract on Base and ETH escrow. Outgoing messages (like deposits) are sent through the BaseL2Gateway which ultimately makes use of Base’s canonical messaging bridge to reach the Arbitrator on L1. Only whitelisted validators can sync messages with zkLink Nova, which also transfer the ETH to it via the respective canonical bridges. Incoming messages (like withdrawals) are validated on Linea first and then sent to this contract through the same path. Whitelisted validators can also relay messages to zkLink without going through the canonical bridge (fast path), which are later cross-checked with the slow path. If the check fails, the system halts.
- This contract stores the following tokens: ETH.
High level interface between the local zkLink contract and Base’s message service.
Manta Pacific
Main entry point for depositing ERC20 tokens from Manta Pacific to zkLink Nova. Outgoing messages and incoming withdrawal validation is delegated to the zkLink contract.
- This contract can store any token.
Main messaging contract on Manta Pacific and ETH escrow. Outgoing messages (like deposits) are sent through the MantaPacificL2Gateway which ultimately makes use of Manta Pacific’s canonical messaging bridge to reach the Arbitrator on L1. Only whitelisted validators can sync messages with zkLink Nova, which also transfer the ETH to it via the respective canonical bridges. Incoming messages (like withdrawals) are validated on Linea first and then sent to this contract through the same path. Whitelisted validators can also relay messages to zkLink without going through the canonical bridge (fast path), which are later cross-checked with the slow path. If the check fails, the system halts.
- This contract stores the following tokens: ETH.
High level interface between the local zkLink contract and Manta Pacific’s message service.
Mantle
Main entry point for depositing ERC20 tokens from Mantle to zkLink Nova. Outgoing messages and incoming withdrawal validation is delegated to the zkLink contract.
- This contract can store any token.
Main messaging contract on Mantle and ETH escrow. Outgoing messages (like deposits) are sent through the MantleL2Gateway which ultimately makes use of Mantle’s canonical messaging bridge to reach the Arbitrator on L1. Only whitelisted validators can sync messages with zkLink Nova, which also transfer the ETH to it via the respective canonical bridges. Incoming messages (like withdrawals) are validated on Linea first and then sent to this contract through the same path. Whitelisted validators can also relay messages to zkLink without going through the canonical bridge (fast path), which are later cross-checked with the slow path. If the check fails, the system halts.
- This contract stores the following tokens: ETH.
High level interface between the local zkLink contract and Mantle’s message service.
Scroll
Main entry point for depositing ERC20 tokens from Scroll to zkLink Nova. Outgoing messages and incoming withdrawal validation is delegated to the zkLink contract.
Main messaging contract on Scroll and ETH escrow. Outgoing messages (like deposits) are sent through the ScrollL2Gateway which ultimately makes use of Scroll’s canonical messaging bridge to reach the Arbitrator on L1. Only whitelisted validators can sync messages with zkLink Nova, which also transfer the ETH to it via the respective canonical bridges. Incoming messages (like withdrawals) are validated on Linea first and then sent to this contract through the same path. Whitelisted validators can also relay messages to zkLink without going through the canonical bridge (fast path), which are later cross-checked with the slow path. If the check fails, the system halts.
High level interface between the local zkLink contract and Scroll’s message service.
Blast
Main entry point for depositing ERC20 tokens from Blast to zkLink Nova. Outgoing messages and incoming withdrawal validation is delegated to the zkLink contract.
- This contract can store any token.
Main messaging contract on Blast and ETH escrow. Outgoing messages (like deposits) are sent through the BlastL2Gateway which ultimately makes use of Blast’s canonical messaging bridge to reach the Arbitrator on L1. Only whitelisted validators can sync messages with zkLink Nova, which also transfer the ETH to it via the respective canonical bridges. Incoming messages (like withdrawals) are validated on Linea first and then sent to this contract through the same path. Whitelisted validators can also relay messages to zkLink without going through the canonical bridge (fast path), which are later cross-checked with the slow path. If the check fails, the system halts.
- This contract stores the following tokens: ETH.
High level interface between the local zkLink contract and Blast’s message service.
ZKsync Era
Main entry point for depositing ERC20 tokens from ZKsync Era to zkLink Nova. Outgoing messages and incoming withdrawal validation is delegated to the zkLink contract. The source code of this contract is not verified on Etherscan.
- This contract can store any token.
Main messaging contract on ZKsync Era and ETH escrow. Outgoing messages (like deposits) are sent through the ZKsync2L2Gateway which ultimately makes use of ZKsync Era’s canonical messaging bridge to reach the Arbitrator on L1. Only whitelisted validators can sync messages with zkLink Nova, which also transfer the ETH to it via the respective canonical bridges. Incoming messages (like withdrawals) are validated on Linea first and then sent to this contract through the same path. Whitelisted validators can also relay messages to zkLink without going through the canonical bridge (fast path), which are later cross-checked with the slow path. If the check fails, the system halts. The source code of this contract is not verified on Etherscan.
- This contract stores the following tokens: ETH.
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on code upgrades (CRITICAL).
Funds can be stolen if the source code of unverified contracts contains malicious code (CRITICAL).
