Search
Search for projects by name or address
 Boba Network
Boba Network
Badges
About
Boba is an OP stack Optimistic Rollup built by the Enya team as core contributors to the Boba Foundation.
Badges
About
Boba is an OP stack Optimistic Rollup built by the Enya team as core contributors to the Boba Foundation.
Why is the project listed in others?
Consequence: projects without a sufficiently decentralized set of challengers rely on few entities to safely update the state. A small set of challengers can collude with the proposer to finalize an invalid state, which can cause loss of funds.
Learn more about the recategorisation here.
2025 Mar 11 — 2026 Mar 11
The section shows the operating costs that L2s pay to Ethereum.
2025 Mar 11 — 2026 Mar 11
This section shows how much data the project publishes to its data-availability (DA) layer over time. The project currently posts data to![]() Ethereum.
Ethereum.
2025 Jun 26 — 2026 Mar 11
This section shows how "live" the project's operators are by displaying how frequently they submit transactions of the selected type. It also highlights anomalies - significant deviations from their typical schedule.
Boba Anchorage Upgrade
2024 Apr 16th
Boba upgrades to Bedrock (OP Stack) and to EIP-4844 data blobs for L1 data availability.
Funds can be stolen if
MEV can be extracted if
Fraud proofs allow actors watching the chain to prove that the state is incorrect. Interactive proofs (INT) require multiple transactions over time to resolve. Only one entity is currently allowed to propose and submit challenges, as only permissioned games are currently allowed.
All of the data needed for proof construction is published on Ethereum L1.
There is no window for users to exit in case of an unwanted regular upgrade since contracts are instantly upgradable.
Only the whitelisted proposers can publish state roots on L1, so in the event of failure the withdrawals are frozen.
All data required for proofs is published on chain
All the data that is used to construct the system state is published on chain in the form of cheap blobs or calldata. This ensures that it will be available for enough time.
- Derivation: Batch submission - OP Mainnet specs
- BatchInbox - address
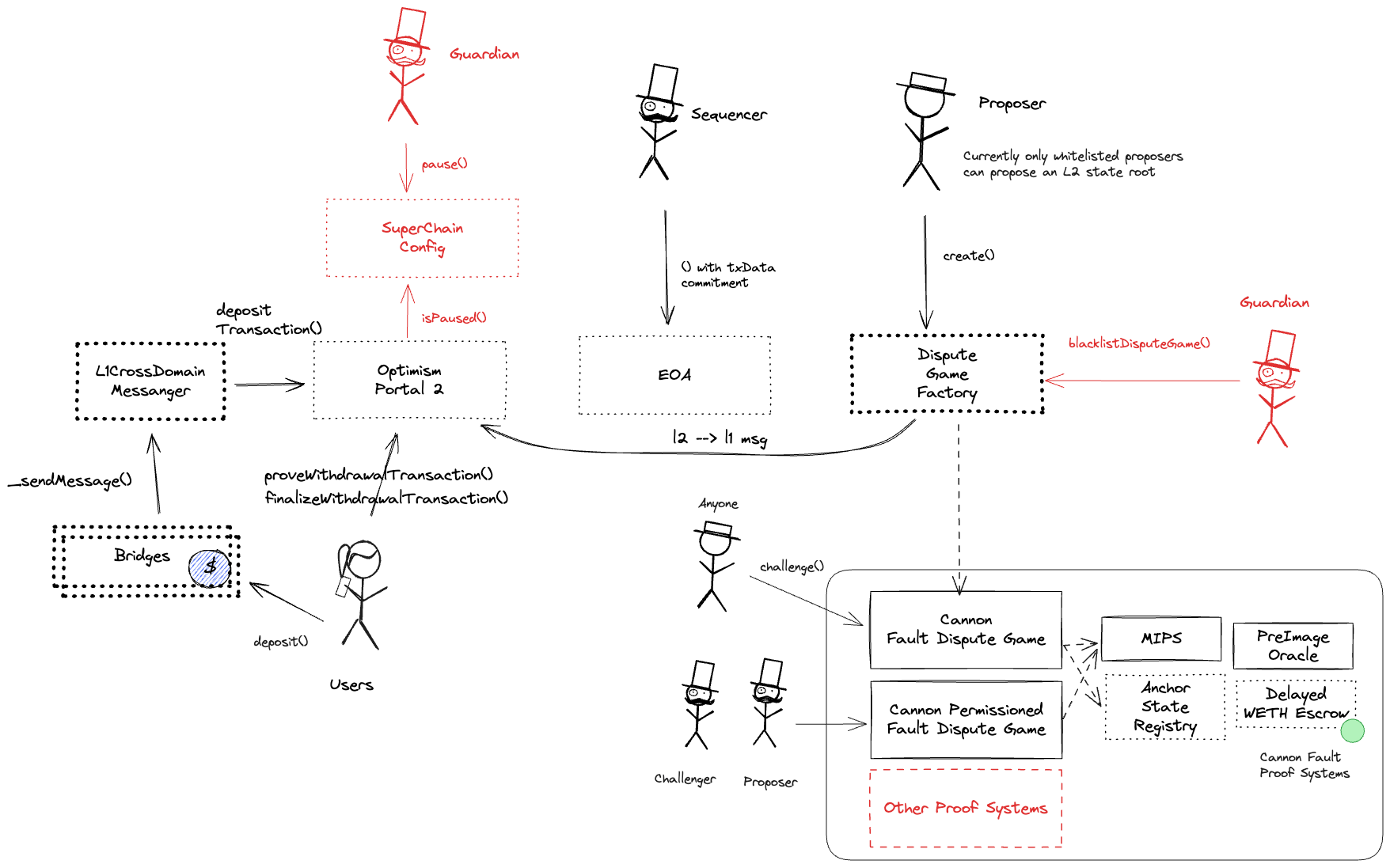
- OptimismPortal2.sol - source code, depositTransaction function
Updates to the system state can be proposed and challenged by permissioned operators only. If a state root passes the challenge period, it is optimistically considered correct and made actionable for withdrawals.
Proposers submit state roots as children of the latest confirmed state root (called anchor state), by calling the create function in the DisputeGameFactory. A state root can have multiple conflicting children. Each proposal requires a stake, currently set to 0.0 ETH, that can be slashed if the proposal is proven incorrect via a fraud proof. Stakes can be withdrawn only after the proposal has been confirmed. A state root gets confirmed if the challenge period has passed and it is not countered.
Challenges are opened to disprove invalid state roots using bisection games. Each bisection move requires a stake that increases expontentially with the depth of the bisection, with a factor of 1.09493. The maximum depth is 73, and reaching it therefore requires a cumulative stake of 0.00 ETH from depth 0. Actors can participate in any challenge by calling the defend or attack functions, depending whether they agree or disagree with the latest claim and want to move the bisection game forward. Actors that disagree with the top-level claim are called challengers, and actors that agree are called defenders. Each actor might be involved in multiple (sub-)challenges at the same time, meaning that the protocol operates with full concurrency. Challengers and defenders alternate in the bisection game, and they pass each other a clock that starts with 3d 12h. If a clock expires, the claim is considered defeated if it was countered, or it gets confirmed if uncountered. Since honest parties can inherit clocks from malicious parties that play both as challengers and defenders (see freeloader claims), if a clock gets inherited with less than 3h, it generally gets extended by 3h with the exception of 6h right before depth 30, and 1d right before the last depth. The maximum clock extension that a top level claim can get is therefore 10d. Since unconfirmed state roots are independent of one another, users can decide to exit with a subsequent confirmed state root if the previous one is delayed. Winners get the entire losers’ stake, meaning that sybils can potentially play against each other at no cost. The final instruction found via the bisection game is then executed onchain in the MIPS one step prover contract who determines the winner. The protocol does not enforce valid bisections, meaning that actors can propose correct initial claims and then provide incorrect midpoints. The protocol can be subject to resource exhaustion attacks (Spearbit 5.1.3).
The system has a centralized operator
MEV can be extracted if the operator exploits their centralized position and frontruns user transactions.
Users can force any transaction
Because the state of the system is based on transactions submitted on the underlying host chain and anyone can submit their transactions there it allows the users to circumvent censorship by interacting with the smart contract on the host chain directly.
Regular exits
The user initiates the withdrawal by submitting a regular transaction on this chain. When a state root containing such transaction is settled, the funds become available for withdrawal on L1 after 3d 12h. Withdrawal inclusion can be proven before state root settlement, but a 7d period has to pass before it becomes actionable. The process of state root settlement takes a challenge period of at least 3d 12h to complete. Finally the user submits an L1 transaction to claim the funds. This transaction requires a merkle proof.
Forced messaging
If the user experiences censorship from the operator with regular L2->L1 messaging they can submit their messages directly on L1. The system is then obliged to service this request or halt all messages, including forced withdrawals from L1 and regular messages initiated on L2. Once the force operation is submitted and if the request is serviced, the operation follows the flow of a regular message.
EVM compatible smart contracts are supported
OP stack chains are pursuing the EVM Equivalence model. No changes to smart contracts are required regardless of the language they are written in, i.e. anything deployed on L1 can be deployed on L2.

Ethereum
Roles:
Allowed to challenge or delete state roots proposed by a Proposer.
Allowed to pause withdrawals. In op stack systems with a proof system, the Guardian can also blacklist dispute games and set the respected game type (permissioned / permissionless).
Allowed to post new state roots of the current layer to the host chain.
Allowed to commit transactions from the current layer to the host chain.
Actors:
A Multisig with 2/3 threshold.
- Can upgrade with no delay
- SystemConfig ProxyAdmin
- OptimismMintableERC20Factory ProxyAdmin
- DelayedWETH ProxyAdmin
- L1CrossDomainMessenger ProxyAdmin
- OptimismPortal2 ProxyAdmin
- SuperchainConfig ProxyAdmin
- L1ERC721Bridge ProxyAdmin
- AnchorStateRegistry ProxyAdmin
- L1StandardBridge ProxyAdmin
- DisputeGameFactory ProxyAdmin
- Can interact with DelayedWETH
- can pull funds from the contract in case of emergency
- Can interact with AddressManager
- set and change address mappings ProxyAdmin
- A Guardian - acting directly
- A Sequencer - acting directly
- A Challenger - acting directly
- A Proposer - acting directly

Ethereum

The dispute game factory allows the creation of dispute games, used to propose state roots and eventually challenge them.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Boba Multisig
This is NOT the shared SuperchainConfig contract of the OP stack Superchain but rather a local fork. It manages the PAUSED_SLOT, a boolean value indicating whether the local chain is paused, and GUARDIAN_SLOT, the address of the guardian which can pause and unpause the system.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Boba Multisig
- guardian: Boba Multisig
Sends messages from host chain to this chain, and relays messages back onto host chain. In the event that a message sent from host chain to this chain is rejected for exceeding this chain’s epoch gas limit, it can be resubmitted via this contract’s replay function.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Boba Multisig
Used to bridge ERC-721 tokens from host chain to this chain.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Boba Multisig
The main entry point to deposit ERC20 tokens from host chain to this chain.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Boba Multisig
All supported tokens in this escrow are included in the value secured calculation.
A helper contract that generates OptimismMintableERC20 contracts on the network it’s deployed to. OptimismMintableERC20 is a standard extension of the base ERC20 token contract designed to allow the L1StandardBridge contracts to mint and burn tokens. This makes it possible to use an OptimismMintableERC20 as this chain’s representation of a token on the host chain, or vice-versa.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Boba Multisig
Contract designed to hold the bonded ETH for each game. It is designed as a wrapper around WETH to allow an owner to function as a backstop if a game would incorrectly distribute funds.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Boba Multisig
- owner: Boba Multisig
The MIPS contract is used to execute the final step of the dispute game which objectively determines the winner of the dispute.
- Roles:
- owner: Boba Multisig
The PreimageOracle contract is used to load the required data from L1 for a dispute game.
Contains the latest confirmed state root that can be used as a starting point in a dispute game.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Boba Multisig
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on code upgrades (CRITICAL).
