Search
Search for projects by name or address
 Polygon zkEVM
Polygon zkEVM
Badges
About
Polygon zkEVM is an EVM-compatible L2 built by Polygon Labs.
Badges
About
Polygon zkEVM is an EVM-compatible L2 built by Polygon Labs.
Why is the project listed in others?
Consequence: projects without a data availability bridge fully rely on single entities (the sequencer) to honestly rely available data roots on Ethereum. A malicious sequencer can collude with the proposer to finalize an unavailable state, which can cause loss of funds.
Consequence: projects without a proper proof system fully rely on single entities to safely update the state. A malicious proposer can finalize an invalid state, which can cause loss of funds.
Learn more about the recategorisation here.
2025 Mar 13 — 2026 Mar 13
The section shows the operating costs that L2s pay to Ethereum.
2025 Mar 13 — 2026 Mar 13
This section shows how "live" the project's operators are by displaying how frequently they submit transactions of the selected type. It also highlights anomalies - significant deviations from their typical schedule.
Polygon zkEVM Etrog upgrade
2024 Feb 13th
Polygon zkEVM is upgraded to the Polygon Etrog version.
Funds can be stolen if
Funds can be lost if
Users can be censored if
There is no mechanism to have transactions be included if the sequencer is down or censoring. Although the functionality exists in the code, it is currently disabled.
Currently the system permits invalid state roots. ‘Pessimistic’ proofs only validate the bridge accounting.
Proof construction and state derivation rely fully on data that is NOT published onchain.
There is no window for users to exit in case of an unwanted regular upgrade since contracts are instantly upgradable.
Only the whitelisted proposers can publish state roots on L1, so in the event of failure the withdrawals are frozen.
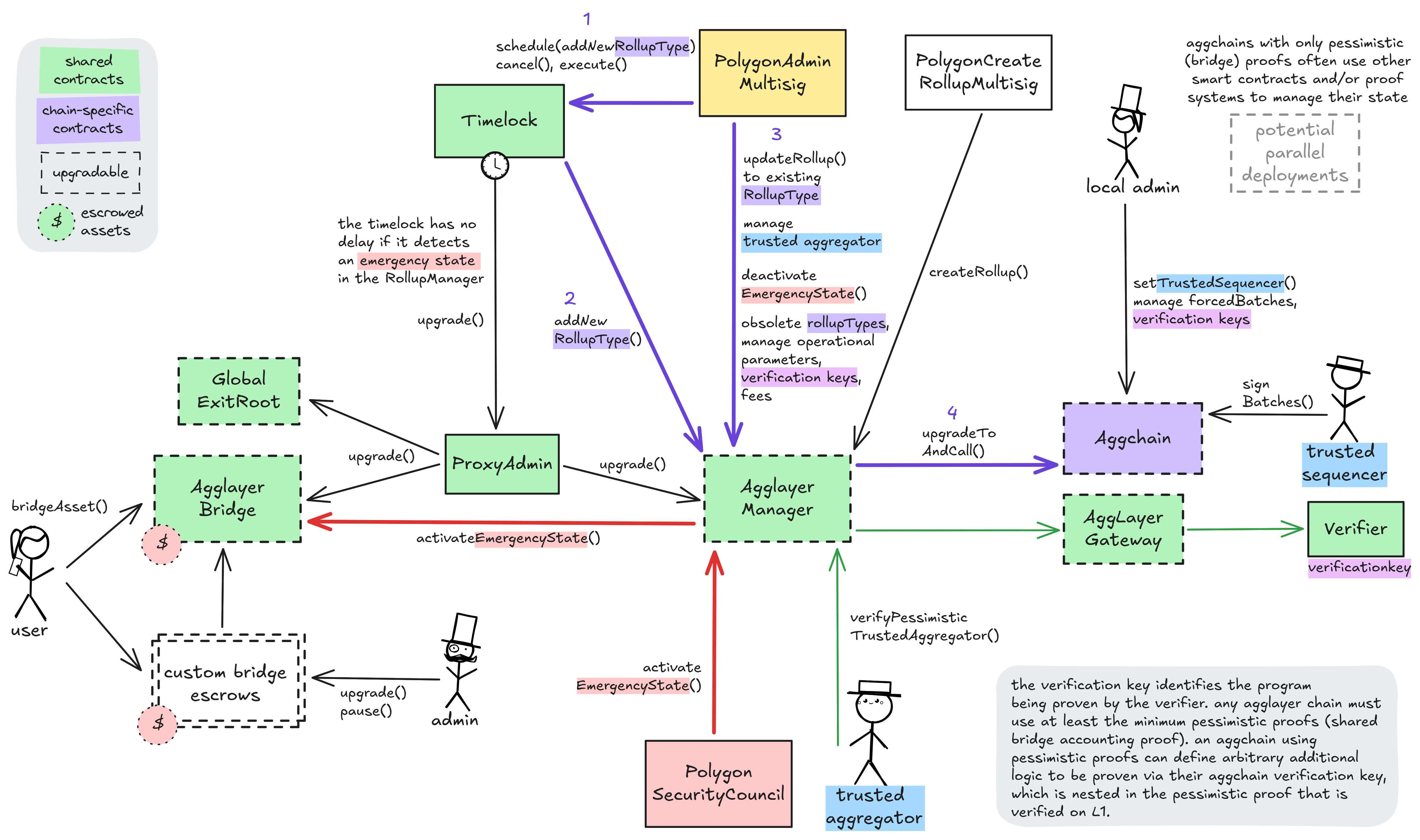
The regular upgrade process for shared system contracts and L2-specific validium contracts starts at the PolygonAdminMultisig. For the shared contracts, they schedule a transaction that targets the ProxyAdmin via the Timelock, wait for 3d and then execute the upgrade. An upgrade of the Layer 2 specific validium contract requires first adding a new rollupType through the Timelock and the AgglayerManager (defining the new implementation and verifier contracts). Now that the rollupType is created, either the local admin or the PolygonAdminMultisig can immediately upgrade the local system contracts to it. Chains using pessimistic proofs often have completely sovereign upgrade paths from the ones described here, but the shared contracts still remain relevant to them because they use them as escrow.
The PolygonSecurityCouncil can expedite the upgrade process by declaring an emergency state. This state pauses both the shared bridge and the AgglayerManager and allows for instant upgrades through the timelock. Accordingly, instant upgrades for all system contracts are possible with the cooperation of the SecurityCouncil. The emergency state has been activated 1 time(s) since inception.
Furthermore, the PolygonAdminMultisig is permissioned to manage the shared trusted aggregator (proposer and prover) for all participating Layer 2s, deactivate the emergency state, obsolete rollupTypes and manage operational parameters and fees in the AgglayerManager directly. The local admin of a specific Aggchain can manage their chain by choosing the trusted sequencer, manage forced batches and set the data availability config. For sovereign chains using pessimistic proofs they can manage any proof logic that might be used on top of the minimal pessimistic one. Creating new Layer 2s (of existing rollupType) is outsourced to the PolygonCreateRollupMultisig but can also be done by the PolygonAdminMultisig. Custom non-shared bridge escrows have their custom upgrade admins listed in the permissions section.
Users can't force any transaction
There is no general mechanism to force the sequencer to include the transaction.
Users can be censored if the operator refuses to include their transactions.
Shared bridge and Pessimistic Proofs
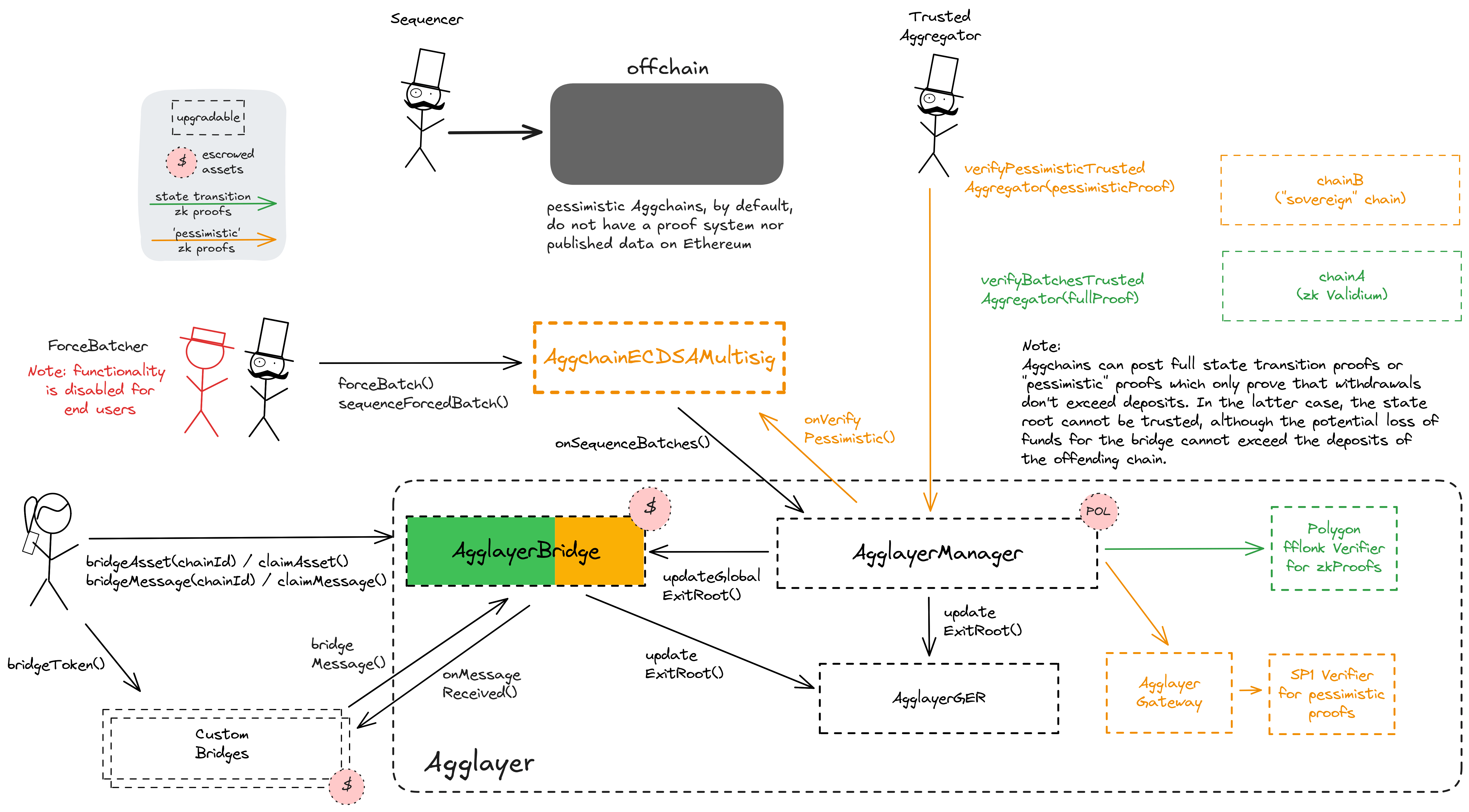
Polygon Agglayer uses a shared bridge escrow for Rollups, Validiums and external chains that opt in to participate in interoperability. Each participating chain needs to provide zk proofs to access any assets in the shared bridge. In addition to the full execution proofs that are used for the state validation of Rollups and Validiums, accounting proofs over the bridges state (Polygon calls them ‘Pessimistic Proofs’) are used by external chains (cdk-erigon-sovereign and cdk-opgeth-sovereign variants). Using the SP1 zkVM by Succinct, even projects without a full proof system on Ethereum are able to share the bridge with any other Aggchain without adding additional trust assumptions.
Funds can be lost if the accounting proof system for the bridge (pessimistic proofs, SP1) is implemented incorrectly.
Funds can be stolen if the operator manipulates the L2 state, which is not validated on Ethereum (CRITICAL).

Ethereum
Roles:
Permissioned to post new state roots and global exit roots accompanied by ZK proofs.
Actors:
A Multisig with 5/9 threshold.
- Can upgrade with 3d delay
- AgglayerGateway Timelock with 3d delay (no delay if in emergency state) → SharedProxyAdmin
- AgglayerBridge Timelock with 3d delay (no delay if in emergency state) → SharedProxyAdmin
- AgglayerManager Timelock with 3d delay (no delay if in emergency state) → SharedProxyAdmin
- AgglayerGER Timelock with 3d delay (no delay if in emergency state) → SharedProxyAdmin
- Can interact with AgglayerGateway
- add new routes from proof selector to verifier / pessimisticVkey for pessimistic proofs with 3d delay Timelock with 3d delay (no delay if in emergency state)
- add or update default aggchain verification keys (aggchainVkey) for any given selectors
- change the aggchainSigners and threshold (a multisig used for permissioned state transitions)
- freeze routes from proof selector to verifier / pessimisticVkey for pessimistic proofs
- Can interact with AgglayerBridge
- upgrade the implementation of wrapped tokens deployed by the bridge with 3d delay Timelock with 3d delay (no delay if in emergency state)
- Can interact with AgglayerManager
- deploy new projects that use predefined rollup types (implementations) and connect them or other Agglayer chains to the PolygonRollupManager
- manage all access control roles, add new rollup types (which are implementation contracts that can then be upgraded to by connected projects), update any connected projects to new rollup types, migrate to pessimistic proofs and rollback batches, connect existing rollups to the PolygonRollupManager with 3d delay Timelock with 3d delay (no delay if in emergency state)
- manage parameters like fees for all connected projects, set the trusted aggregator, stop the emergency state, update projects and obsolete rollup types
- Can interact with Timelock
- propose, cancel and execute transactions in the timelock, manage all access control roles and change the minimum delay with 6d delay or with 3d delay Timelock with 3d delay (no delay if in emergency state) with 3d delay (no delay if in emergency state) - or - acting directly with 3d delay (no delay if in emergency state)
Participants (9):
0xEB5E…EA720xAb35…235E0xED7c…B5a20xdFEd…56Da0xffbf…32380xeD44…dB370x516e…46B70xA0B0…f2270x8B9F…782BA Multisig with 6/8 threshold.
- Can interact with AgglayerManager
- activate the emergency state in the PolygonRollupManager and in the shared bridge immediately, effectively pausing all projects connected to them and making system contracts instantly upgradable
Participants (8):
0xFe45…2e4b0xaF46…261D0xBDc2…FEFf0x4c16…88910x3ab9…D6220x49c1…0E860x9F7d…86A00x2188…1C28A Multisig with 3/5 threshold.
- Can interact with AgglayerManager
- deploy new projects that use predefined rollup types (implementations) and connect them or other Agglayer chains to the PolygonRollupManager
A Multisig with 5/10 threshold.
- Can upgrade with no delay
- daiBridge
- usdcBridge
- wstETHBridge
- Can interact with AggchainECDSAMultisig
- sign state transitions (replaces state validation for this aggchain)
- A trusted Aggregator - acting directly

Ethereum
A verifier gateway for pessimistic proofs. Manages a map of chains and their verifier keys and is used to route proofs based on the first 4 bytes of proofBytes data in a proof submission. The SP1 verifier is used for all proofs.
- Roles:
- addPpRoute: Timelock; ultimately PolygonAdminMultisig
- admin: SharedProxyAdmin; ultimately PolygonAdminMultisig
- aggchainDefaultVKey: PolygonAdminMultisig
- alMultisig: PolygonAdminMultisig
- freezePpRoute: PolygonAdminMultisig
The shared bridge contract, escrowing user funds sent to Agglayer chains. It is usually mirrored on each chain and can be used to transfer both ERC20 assets and arbitrary messages.
- Roles:
- admin: SharedProxyAdmin; ultimately PolygonAdminMultisig
- proxiedTokensManager: Timelock; ultimately PolygonAdminMultisig
All supported tokens in this escrow are included in the value secured calculation.
The central shared managing contract for Polygon Agglayer chains. This contract coordinates chain deployments and proof validation. All connected Layer 2s can be globally paused by activating the ‘Emergency State’. This can be done by the PolygonSecurityCouncil or by anyone after 1 week of inactive verifiers.
- Roles:
- admin: SharedProxyAdmin; ultimately PolygonAdminMultisig
- createRollup: PolygonAdminMultisig, PolygonCreateRollupMultisig
- defaultAdmin: Timelock; ultimately PolygonAdminMultisig
- emergencyCouncilAdmin: PolygonSecurityCouncil
- trustedAggregator: EOA 2, EOA 3
- tweakParameters: PolygonAdminMultisig
A merkle tree storage contract aggregating state roots of each participating Layer 2, thus creating a single global merkle root representing the global state of the Agglayer, the ‘global exit root’. The global exit root is synchronized to all connected Layer 2s to help with their interoperability.
- Roles:
- admin: SharedProxyAdmin; ultimately PolygonAdminMultisig
A timelock with access control. In the case of an activated emergency state in the AgglayerManager, all transactions through this timelock are immediately executable. The current minimum delay is 3d.
- Roles:
- timelockAdmin: PolygonAdminMultisig (no delay if in emergency state), Timelock (no delay if in emergency state); ultimately PolygonAdminMultisig (no delay if in emergency state)




Extension contract of the AgglayerBridge for asset metadata…
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on code upgrades (CRITICAL).
