Search
Search for projects by name or address
 Phala
Phala
Badges
About
Phala is a cloud computing protocol which aims at offering developers a secure and efficient platform for deploying and managing AI-ready applications in a trusted environment (TEE). Phala rollup on Ethereum leverages the Op-Succinct stack, a... combination of OP stack contracts and Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZK) using the SP1 zkVM.
Badges
About
Phala is a cloud computing protocol which aims at offering developers a secure and efficient platform for deploying and managing AI-ready applications in a trusted environment (TEE). Phala rollup on Ethereum leverages the Op-Succinct stack, a... combination of OP stack contracts and Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZK) using the SP1 zkVM.
2025 Mar 08 — 2026 Mar 08
The section shows the operating costs that L2s pay to Ethereum.
2025 Mar 08 — 2026 Mar 08
This section shows how much data the project publishes to its data-availability (DA) layer over time. The project currently posts data to![]() Ethereum.
Ethereum.
2025 Mar 08 — 2026 Mar 08
This section shows how "live" the project's operators are by displaying how frequently they submit transactions of the selected type. It also highlights anomalies - significant deviations from their typical schedule.
Switched back to Validity Proofs
2026 Feb 2nd
Phala switched back to OPSuccinct (SP1 ZK proofs).
Switched to Optimistic Proofs
2026 Jan 20th
Phala switched from OPSuccinct (SP1 ZK proofs) to PermissionedDisputeGame (optimistic fault proofs).
Funds can be stolen if
Funds can be frozen if
MEV can be extracted if
STARKs and SNARKs are zero knowledge proofs that ensure state correctness. STARKs proofs are wrapped in SNARKs proofs for efficiency. SNARKs require a trusted setup.
All of the data needed for proof construction is published on Ethereum L1.
There is no window for users to exit in case of an unwanted regular upgrade since contracts are instantly upgradable.
Only the whitelisted proposers can publish state roots on L1, so in the event of failure the withdrawals are frozen.
All data required for proofs is published on chain
All the data that is used to construct the system state is published on chain in the form of cheap blobs or calldata. This ensures that it will be available for enough time.
- Derivation: Batch submission - OP Mainnet specs
- BatchInbox - address
- OptimismPortal2.sol - source code, depositTransaction function
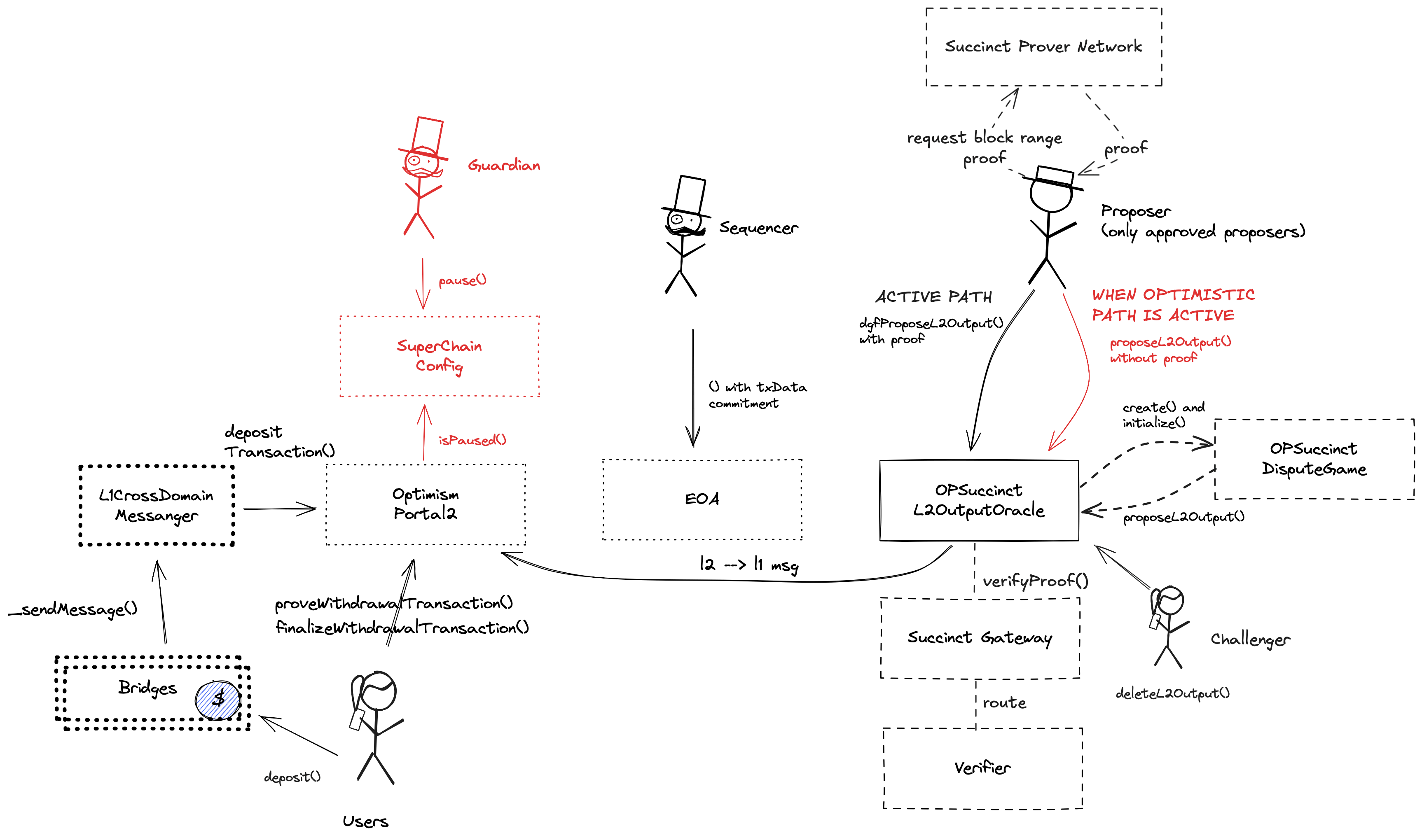
Each update to the system state must be accompanied by a ZK proof that ensures that the new state was derived by correctly applying a series of valid user transactions to the previous state. These proofs are then verified on Ethereum by a smart contract. Through the SuccinctL2OutputOracle, the system also allows to switch to an optimistic mode, in which no proofs are required and a challenger can challenge the proposed output state root within the finalization period.
Funds can be stolen if in non-optimistic mode, the validity proof cryptography is broken or implemented incorrectly.
Funds can be stolen if optimistic mode is enabled and no challenger checks the published state.
Funds can be frozen if the permissioned proposer fails to publish state roots to the L1.
The system has a centralized operator
MEV can be extracted if the operator exploits their centralized position and frontruns user transactions.
Users can force any transaction
Because the state of the system is based on transactions submitted on the underlying host chain and anyone can submit their transactions there it allows the users to circumvent censorship by interacting with the smart contract on the host chain directly.
Regular messaging
Funds can be frozen if the centralized validator goes down. Users cannot produce blocks themselves and exiting the system requires new block production (CRITICAL).
Forced messaging
If the user experiences censorship from the operator with regular L2->L1 messaging they can submit their messages directly on L1. The system is then obliged to service this request or halt all messages, including forced withdrawals from L1 and regular messages initiated on L2. Once the force operation is submitted and if the request is serviced, the operation follows the flow of a regular message.
EVM compatible smart contracts are supported
OP stack chains are pursuing the EVM Equivalence model. No changes to smart contracts are required regardless of the language they are written in, i.e. anything deployed on L1 can be deployed on L2.

Ethereum
Roles:
Allowed to challenge or delete state roots proposed by a Proposer.
Allowed to pause withdrawals. In op stack systems with a proof system, the Guardian can also blacklist dispute games and set the respected game type (permissioned / permissionless).
Allowed to post new state roots of the current layer to the host chain.
Allowed to commit transactions from the current layer to the host chain.
Actors:
A Multisig with 4/13 threshold.
- Can upgrade with no delay
- SuperchainConfig ProxyAdmin
- L1CrossDomainMessenger ProxyAdmin
- DisputeGameFactory ProxyAdmin
- L1StandardBridge ProxyAdmin
- OptimismPortal2 ProxyAdmin
- L1ERC721Bridge ProxyAdmin
- OPSuccinctL2OutputOracle ProxyAdmin
- DelayedWETH ProxyAdmin
- AnchorStateRegistry ProxyAdmin
- SystemConfig ProxyAdmin
- OptimismMintableERC20Factory ProxyAdmin
- Can interact with AddressManager
- set and change address mappings ProxyAdmin
- Can interact with OPSuccinctL2OutputOracle
- can toggle between the optimistic mode and not optimistic (ZK) mode
- Can interact with SystemConfig
- A Challenger - acting directly
- A Guardian - acting directly
Participants (13):
0xA9FC…8d090x3816…Cf070x6BB4…83A60x2103…911c0x65D1…60070x8117…E7Ac0xA073…bda20xF331…647D0xa400…e6e40x3840…Fd5f0xa0C6…90380xefCf…dD5C0x4D80…5BAe- A Sequencer - acting directly
- A Proposer - acting directly
Arbitrum One
Actors:
Base Chain
Actors:

Ethereum
The dispute game factory allows the creation of dispute games, used to propose state roots and eventually challenge them.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Conduit Multisig 1
The OptimismPortal contract is the main entry point to deposit funds from L1 to L2. It also allows to prove and finalize withdrawals. It specifies which game type can be used for withdrawals, which currently is the 6.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Conduit Multisig 1
- This contract stores the following tokens: ETH.
This is NOT the shared SuperchainConfig contract of the OP stack Superchain but rather a local fork. It manages pause states for each chain connected to it, as well as a global pause state for all chains. The guardian role can pause either separately, but each pause expires after 3mo 1d if left untouched.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Conduit Multisig 1
- guardian: Conduit Multisig 1
Sends messages from host chain to this chain, and relays messages back onto host chain. In the event that a message sent from host chain to this chain is rejected for exceeding this chain’s epoch gas limit, it can be resubmitted via this contract’s replay function.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Conduit Multisig 1
The main entry point to deposit ERC20 tokens from host chain to this chain.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Conduit Multisig 1
- This contract can store any token.
Used to bridge ERC-721 tokens from host chain to this chain.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Conduit Multisig 1
- Roles:
- owner: Conduit Multisig 1
The PreimageOracle contract is used to load the required data from L1 for a dispute game.
A dispute game wrapper around OPSuccinctL2OutputOracle. It is needed to comply with OptimismPortal2 requirement to have a DisputeGameFactory. Whenever a new game is created, an SP1 proof is immediately verified, so in fact there is no optimistic dispute game happening.
The MIPS contract is used to execute the final step of the dispute game which objectively determines the winner of the dispute.
Contains a list of proposed state roots which Proposers assert to be a result of block execution. The SuccinctL2OutputOracle modifies the L2OutputOracle to support whenNotOptimistic mode, in which a validity proof can be passed as input argument to the proposeL2Output function.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Conduit Multisig 1
- owner: Conduit Multisig 1
- proposer: EOA 2
Contract designed to hold the bonded ETH for each game. It is designed as a wrapper around WETH to allow an owner to function as a backstop if a game would incorrectly distribute funds.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Conduit Multisig 1
Contains the latest confirmed state root that can be used as a starting point in a dispute game. It specifies which game type can be used for withdrawals, which currently is the 6.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Conduit Multisig 1
A helper contract that generates OptimismMintableERC20 contracts on the network it’s deployed to. OptimismMintableERC20 is a standard extension of the base ERC20 token contract designed to allow the L1StandardBridge contracts to mint and burn tokens. This makes it possible to use an OptimismMintableERC20 as this chain’s representation of a token on the host chain, or vice-versa.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately Conduit Multisig 1
Arbitrum One
Base Chain
Value Secured is calculated based on these smart contracts and tokens:
Main entry point for users depositing ERC20 token that do not require custom gateway.
Main entry point for users depositing ETH.
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on code upgrades (CRITICAL).
