Search
Search for projects by name or address
 tanX
tanX
Critical contract references can be changed by an EOA which could result in the loss of all funds.
Badges
About
tanX is a DEX powered by StarkEx technology.
Badges
About
tanX is a DEX powered by StarkEx technology.
Why is the project listed in others?
Consequence: projects without a sufficiently decentralized data availability committee rely on few entities to safely attest data availability on Ethereum. A small set of entities can collude with the proposer to finalize an unavailable state, which can cause loss of funds.
Learn more about the recategorisation here.
2025 Feb 26 — 2026 Feb 26
Funds can be stolen if
Funds can be lost if
Users can be censored if
MEV can be extracted if
STARKs are zero knowledge proofs that ensure state correctness.
Proof construction relies fully on data that is NOT published onchain. There exists a Data Availability Committee (DAC) with a threshold of 2/4 that is tasked with protecting and supplying the data.
There is no window for users to exit in case of an unwanted regular upgrade since contracts are instantly upgradable.
Users are able to trustlessly exit by submitting a Merkle proof of funds.
Set of parties responsible for signing and attesting to the availability of data.
There are no onchain assets at risk of being slashed in case of a data withholding attack, and the committee members are not publicly known.
There is no fraud detection mechanism in place. A data withholding attack can only be detected by nodes downloading the full data from the DA layer.
The committee does not meet basic security standards, either due to insufficient size, lack of member diversity, or poorly defined threshold parameters. The system lacks an effective DA bridge and it is reliant on the assumption of an honest sequencer, creating significant risks to data integrity and availability.
Anyone can relay data availability commitments to the DA bridge. In case of current relayer failure, users can collect attestations from committee members and propose new data availability commitments to the DA bridge.
Architecture

The Starkware application utilizes a data availability solution that relies on a Committee Service to ensure data persistence. This architecture comprises the following components:
- Availability Gateway: The primary interface provided by the operator for committee members to access new batch information and submit signed availability claims.
- Data Availability Committee (DAC): A group of nodes responsible for storing state data associated with each Merkle root and attesting to data availability by signing claims.
- Data Batches: Collections of transactions processed in batches that update the state of accounts, resulting in a new Merkle root representing the updated state.
Committee members run services that interact with the Availability Gateway to obtain information about new batches and submit their signed availability claims. Each batch includes a unique batch_id, a reference to a previous batch, and a list of account updates. Committee members combine this information with data from the reference batch to compute the new state and verify the Merkle root.
When the operator produces a new batch, it must be signed by a minimum number of committee members—as defined by the application’s configuration—for it to be accepted onchain. This includes all members designated as mandatory signers. If the operator attempts to submit a batch without the required signatures, it will be rejected, thereby ensuring that data remains available and consistent.
Committee members are expected to maintain a database that stores the data associated with each batch, making use of storage solutions with a replication factor of at least 2.
DA Bridge Architecture

The DA commitments are posted to the destination chain, using the Committee Verifier contract as a DA bridge. The DA commitment consists of a data hash of the transaction batch the Committee has signed off on and a concatenation of ec-signatures by signatories.
The Committee Verifier contract verifies the signatures and the data hash and if the required threshold of Committee members has signed off on the data, the hash is stored as a registeredFact in the StarkEx contract. In a separate transaction, the operator calls the updateState() function on the StarkEx contract to update the state. Before the state update is accepted, the StarkEx contract verifies the transaction public inputs by calling the isValid() function, which verifies the hash derived from state update inputs matches the hash stored by the Committee Verifier contract.
Funds can be lost if a malicious committee signs a data availability attestation for an unavailable transaction batch.
Each update to the system state must be accompanied by a ZK proof that ensures that the new state was derived by correctly applying a series of valid user transactions to the previous state. These proofs are then verified on Ethereum by a smart contract. The system state is represented using Merkle roots.
Program Hashes
Name | Hash | Repository | Verification | Used in | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
168306...3513 | Code unknown | None | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
378893...4778 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
989994...0176 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
348018...5714 | Code unknown | None | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
303597...6711 | Code unknown | None | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
358503...1237 | Code unknown | None | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
160268...8631 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
110431...7907 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The system has a centralized operator
MEV can be extracted if the operator exploits their centralized position and frontruns user transactions.
Users can force exit the system
Force exit allows the users to escape censorship by withdrawing their funds. The system allows users to force the withdrawal of funds by submitting a request directly to the contract onchain. The request must be served within a defined time period. If this does not happen, the system will halt regular operation and permit trustless withdrawal of funds.
Users can be censored if the operator refuses to include their transactions. However, there exists a mechanism to independently exit the system.
Regular exit
The user initiates the withdrawal by submitting a regular transaction on this chain. When the block containing that transaction is settled the funds become available for withdrawal on L1. ZK proofs are required to settle blocks. Finally the user submits an L1 transaction to claim the funds. When withdrawing NFTs they are minted on L1.
Forced exit
If the user experiences censorship from the operator with regular exit they can submit their withdrawal requests directly on L1. The system is then obliged to service this request. Once the force operation is submitted and if the request is serviced, the operation follows the flow of a regular exit.
Emergency exit
If the enough time deadline passes and the forced exit is still ignored the user can put the system into a frozen state, disallowing further state updates. In that case everybody can withdraw by submitting a merkle proof of their funds with their L1 transaction.

Ethereum
Roles:
Permissioned to regularly update the state roots of the L2 on L1. Each state update must have been proven via the SHARP verifier and contains commitments to the data that is itself kept offchain.
Actors:
A Multisig with 2/4 threshold.
- Can upgrade with 8d delay
- SHARPVerifierCallProxy - acting directly with 8d delay
- Can interact with SHARPVerifierCallProxy
- manage the upgrade admin amd access control roles
- set custom implementations for specific operators (changes the verifier based on who calls it)
- Can upgrade with no delay
- StarkExchange
- Can interact with StarkExchange
- manage the token admin role
- A Governor - acting directly
- Can interact with StarkExchange
- Can regsiter new tokens for deposits and withdrawals
- An Operator - acting directly

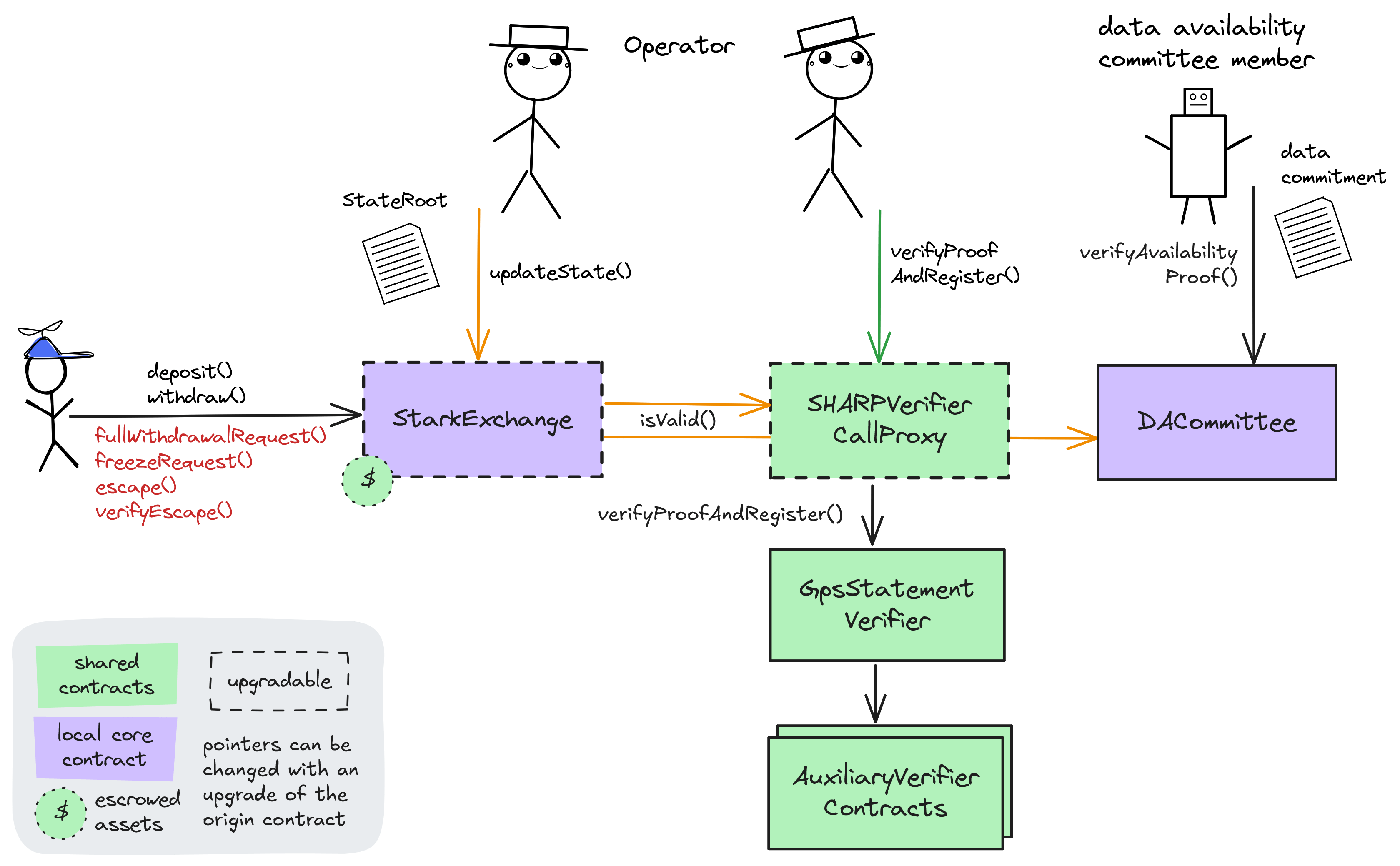
Ethereum
Central Validium contract. Receives (verified) state roots from the Operator, allows users to consume L2 -> L1 messages and send L1 -> L2 messages. Critical configuration values for the L2’s logic are defined here by various governance roles.
- Roles:
- admin: EOA 1
- operators: EOA 3
- tokenAdmins: EOA 2
- This contract can store any token.
Data Availability Committee (DAC) contract verifying and storing data availability claims from DAC Members (via a multisignature check). The threshold of valid signatures is 2.
Upgradable call proxy contract through which the SHARPVerifier can be called. A call proxy does not delegatecall and the storage context remains at the target contract. It allows SHARP Multisig to change the otherwise immutable verifier contract with 8d delay.
- Roles:
- admin: SHARP Multisig
- appGovernor: SHARP Multisig
- governanceAdmin: SHARP Multisig
Shared Starkware SHARP verifier used collectively by Starknet and other SN stack and StarkEx projects. It receives STARK proofs from the Prover and verifies the integrity of the offchain execution including a correctly computed state root which is part of the Program Output.
Adapter between the core contract and the SHARPVerifierCallProxy. Stores the Cairo programHash (16830627573509542901909952446321116535677491650708854009406762893086223513).
Helper contract for registering limit orders from L1.
Auxiliary to the SHARPVerifier contract: Verified ‘memory fact pages’ get stored here. This is important as it registers all necessary onchain data produced by the verifier.
Value Secured is calculated based on these smart contracts and tokens:
Main entry point for users’ deposits.
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. There is no delay on code upgrades (CRITICAL).
Program Hashes
Name | Hash | Repository | Verification | Used in | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
168306...3513 | Code unknown | None | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
378893...4778 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
989994...0176 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
348018...5714 | Code unknown | None | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
303597...6711 | Code unknown | None | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
358503...1237 | Code unknown | None | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
160268...8631 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
110431...7907 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
