Search
Search for projects by name or address
 OP Mainnet
OP Mainnet
Badges
About
OP Mainnet is an EVM-equivalent Optimistic Rollup. It aims to be fast, simple, and secure.
Badges
About
OP Mainnet is an EVM-equivalent Optimistic Rollup. It aims to be fast, simple, and secure.
2025 Mar 07 — 2026 Mar 07
The section shows the operating costs that L2s pay to Ethereum.
2025 Mar 07 — 2026 Mar 07
This section shows how much data the project publishes to its data-availability (DA) layer over time. The project currently posts data to![]() Ethereum.
Ethereum.
2025 Mar 07 — 2026 Mar 07
This section shows how "live" the project's operators are by displaying how frequently they submit transactions of the selected type. It also highlights anomalies - significant deviations from their typical schedule.
Upgrade 17 - Jovian Hardfork and Fusaka Readiness
2025 Nov 25th
A protocol upgrade improving fee mechanisms and preparing the OP Stack for the Fusaka hardfork.
Upgrade #16 Interop Contracts + Upgrades to Cannon
2025 Jul 14th
Optimism readies Superchain interop and boosts security, scale, and Cannon.
Funds can be stolen if
MEV can be extracted if
Fraud proofs allow actors watching the chain to prove that the state is incorrect. Interactive proofs (INT) require multiple transactions over time to resolve.
All of the data needed for proof construction is published on Ethereum L1.
There is no exit window for users to exit in case of unwanted regular upgrades as they are initiated by the Security Council with instant upgrade power and without proper notice.
All data required for proofs is published on chain
All the data that is used to construct the system state is published on chain in the form of cheap blobs or calldata. This ensures that it will be available for enough time.
- Derivation: Batch submission - OP Mainnet specs
- BatchInbox - address
- OptimismPortal2.sol - source code, depositTransaction function
Data batches are compressed using the zlib algorithm with best compression level.
Updates to the system state can be proposed and challenged by anyone who has sufficient funds. If a state root passes the challenge period, it is optimistically considered correct and made actionable for withdrawals.
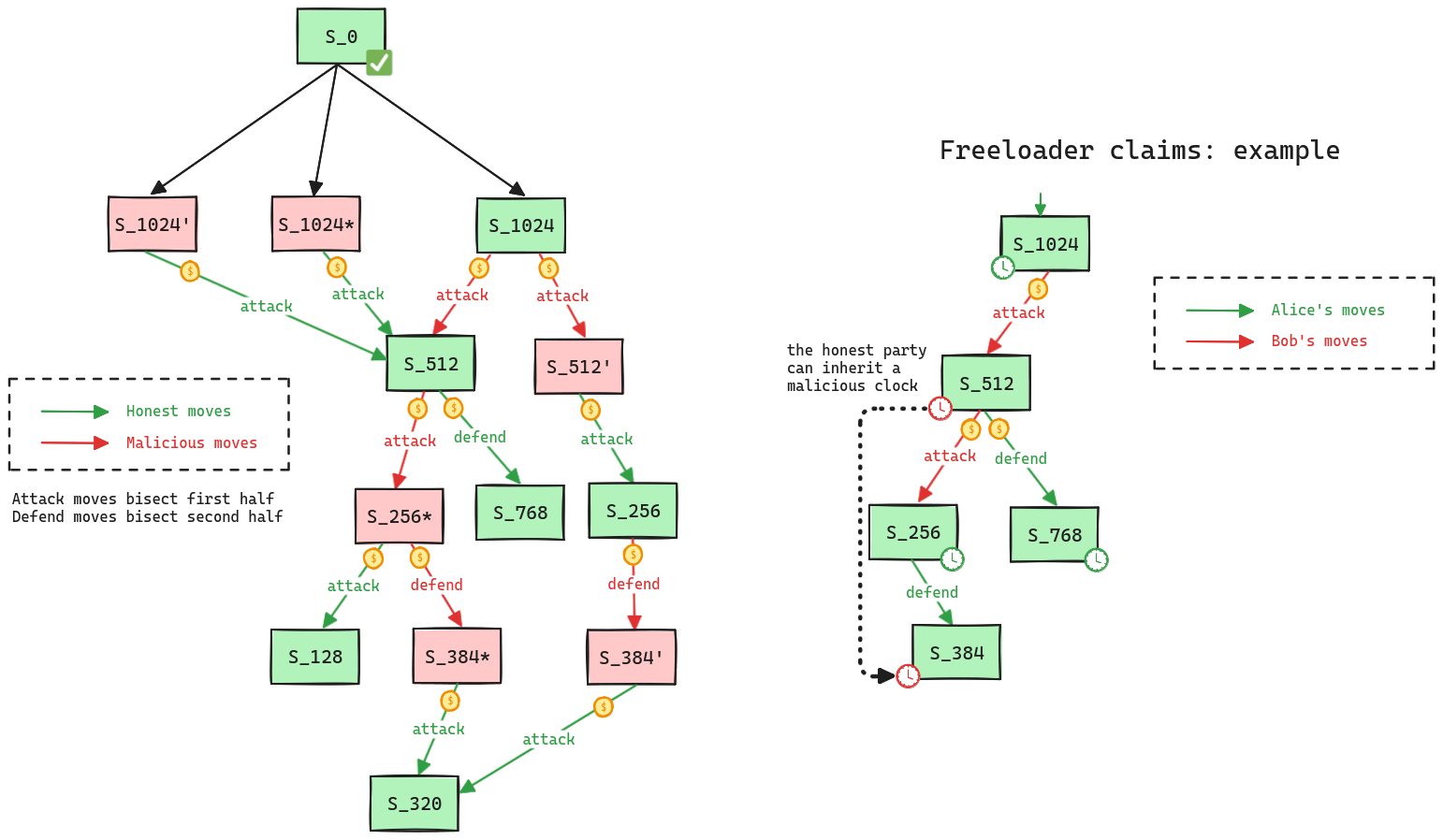
Proposers submit state roots as children of the latest confirmed state root (called anchor state), by calling the create function in the DisputeGameFactory. A state root can have multiple conflicting children. Each proposal requires a stake, currently set to 0.08 ETH, that can be slashed if the proposal is proven incorrect via a fraud proof. Stakes can be withdrawn only after the proposal has been confirmed. A state root gets confirmed if the challenge period has passed and it is not countered.
Challenges are opened to disprove invalid state roots using bisection games. Each bisection move requires a stake that increases expontentially with the depth of the bisection, with a factor of 1.09493. The maximum depth is 73, and reaching it therefore requires a cumulative stake of 691.43 ETH from depth 0. Actors can participate in any challenge by calling the defend or attack functions, depending whether they agree or disagree with the latest claim and want to move the bisection game forward. Actors that disagree with the top-level claim are called challengers, and actors that agree are called defenders. Each actor might be involved in multiple (sub-)challenges at the same time, meaning that the protocol operates with full concurrency. Challengers and defenders alternate in the bisection game, and they pass each other a clock that starts with 3d 12h. If a clock expires, the claim is considered defeated if it was countered, or it gets confirmed if uncountered. Since honest parties can inherit clocks from malicious parties that play both as challengers and defenders (see freeloader claims), if a clock gets inherited with less than 3h, it generally gets extended by 3h with the exception of 6h right before depth 30, and 1d right before the last depth. The maximum clock extension that a top level claim can get is therefore 10d. Since unconfirmed state roots are independent of one another, users can decide to exit with a subsequent confirmed state root if the previous one is delayed. Winners get the entire losers’ stake, meaning that sybils can potentially play against each other at no cost. The final instruction found via the bisection game is then executed onchain in the MIPS one step prover contract who determines the winner. The protocol does not enforce valid bisections, meaning that actors can propose correct initial claims and then provide incorrect midpoints. The protocol can be subject to resource exhaustion attacks (Spearbit 5.1.3).
Program Hashes
Name | Hash | Repository | Verification | Used in | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x033c...bb6e | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
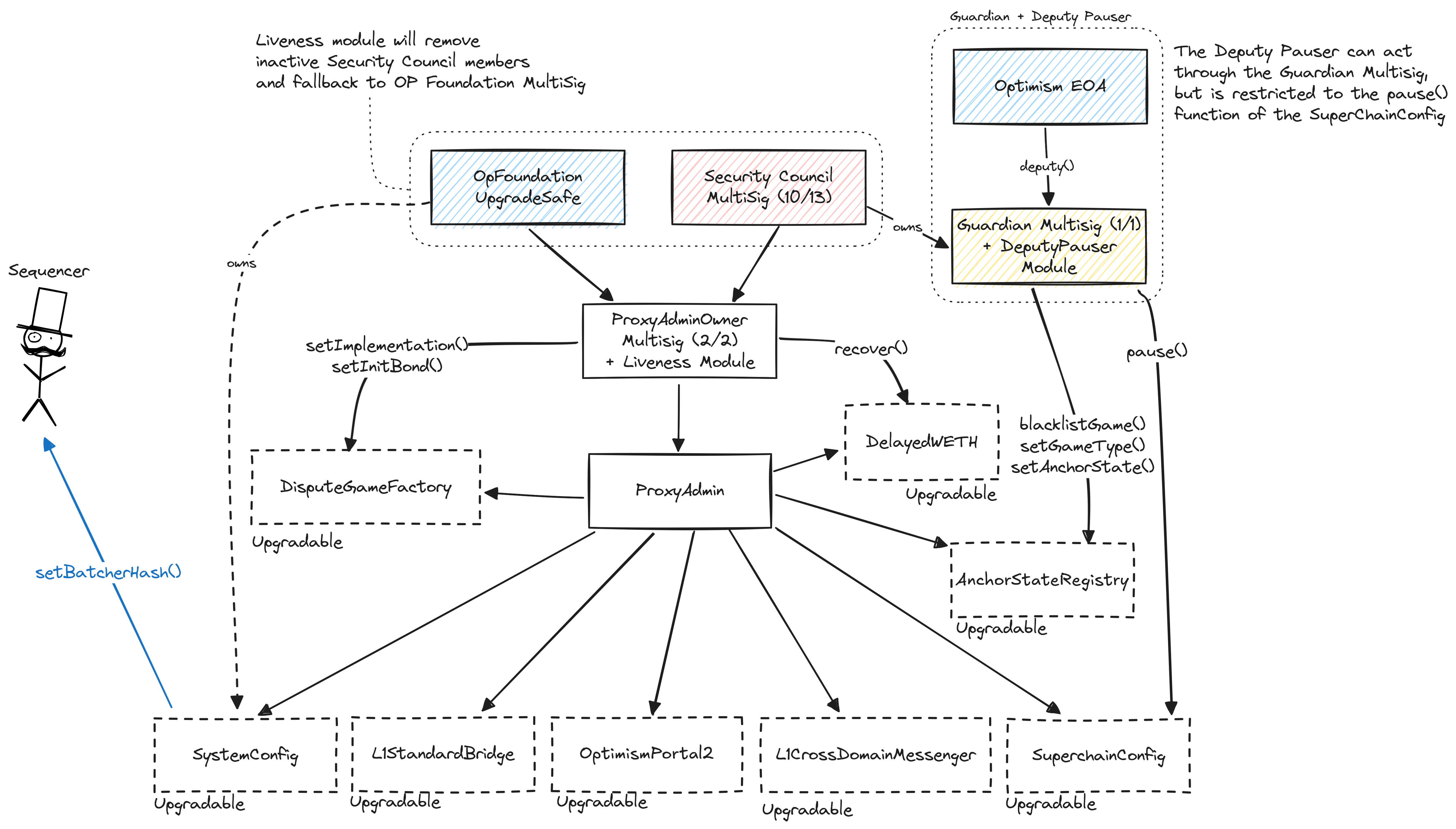
All contracts are upgradable by the SuperchainProxyAdmin which is controlled by a 2/2 multisig composed by the Optimism Foundation and a Security Council. The Guardian role is assigned to the Security Council multisig, with a Safe Module that limits the Optimism Foundation to act through it to stop withdrawals in the whole Superchain or specific individual chains. Each pause automatically expires after 3 months if not extended or unpaused by the Security Council. The Security Council can remove the module if the Foundation becomes malicious. The single Sequencer actor can be modified by the OpFoundationOperationsSafe via the SystemConfig contract. The SuperchainProxyAdminOwner can recover dispute bonds in case of bugs that would distribute them incorrectly.
At the moment, for regular upgrades, the DAO signals its intent by voting on upgrade proposals, but has no direct control over the upgrade process.
The system has a centralized operator
MEV can be extracted if the operator exploits their centralized position and frontruns user transactions.
Users can force any transaction
Because the state of the system is based on transactions submitted on the underlying host chain and anyone can submit their transactions there it allows the users to circumvent censorship by interacting with the smart contract on the host chain directly.
Regular exits
The user initiates the withdrawal by submitting a regular transaction on this chain. When a state root containing such transaction is settled, the funds become available for withdrawal on L1 after 3d 12h. Withdrawal inclusion can be proven before state root settlement, but a 7d period has to pass before it becomes actionable. The process of state root settlement takes a challenge period of at least 3d 12h to complete. Finally the user submits an L1 transaction to claim the funds. This transaction requires a merkle proof.
Forced messaging
If the user experiences censorship from the operator with regular L2->L1 messaging they can submit their messages directly on L1. The system is then obliged to service this request or halt all messages, including forced withdrawals from L1 and regular messages initiated on L2. Once the force operation is submitted and if the request is serviced, the operation follows the flow of a regular message.
EVM compatible smart contracts are supported
OP stack chains are pursuing the EVM Equivalence model. No changes to smart contracts are required regardless of the language they are written in, i.e. anything deployed on L1 can be deployed on L2.

Ethereum
Roles:
Allowed to pause withdrawals. In op stack systems with a proof system, the Guardian can also blacklist dispute games and set the respected game type (permissioned / permissionless).
- OpFoundationUpgradeSafe has the role if the number of Optimism Security Council members falls below 8
- SaferSafes has the role if the number of Optimism Security Council members falls below 8
- Optimism EOA 1 has the role though restricted to the SuperchainConfig’s
pause()function
Allowed to commit transactions from the current layer to the host chain.
Actors:
A Multisig with 2/2 threshold.
- Can upgrade with no delay
- SystemConfig SuperchainProxyAdmin
- AnchorStateRegistry SuperchainProxyAdmin
- L1CrossDomainMessenger SuperchainProxyAdmin
- ETHLockbox SuperchainProxyAdmin
- L1ERC721Bridge SuperchainProxyAdmin
- OptimismMintableERC20Factory SuperchainProxyAdmin
- SuperchainConfig SuperchainProxyAdmin
- L1StandardBridge SuperchainProxyAdmin
- OptimismPortal2 SuperchainProxyAdmin
- DelayedWETH SuperchainProxyAdmin
- DelayedWETH SuperchainProxyAdmin
- DisputeGameFactory SuperchainProxyAdmin
- Can interact with AddressManager
- set and change address mappings SuperchainProxyAdmin
A Multisig with 5/7 threshold. It uses the following modules: SaferSafes (A Gnosis Safe module combining LivenessModule and TimelockGuard. Provides liveness checks where a fallback owner can challenge and take over if Safe owners are unresponsive, plus optional timelock delays for transaction scheduling). Member of SuperchainProxyAdminOwner.
- Can interact with SystemConfig
- A Guardian LivenessModule if the number of Optimism Security Council members falls below 8 → Optimism Security Council → Optimism Guardian Multisig
A Gnosis Safe module combining LivenessModule and TimelockGuard. Provides liveness checks where a fallback owner can challenge and take over if Safe owners are unresponsive, plus optional timelock delays for transaction scheduling.
- Can interact with SystemConfig
- A Guardian OpFoundationUpgradeSafe → LivenessModule if the number of Optimism Security Council members falls below 8 → Optimism Security Council → Optimism Guardian Multisig
A Multisig with 10/13 threshold. It uses the following modules: LivenessModule (used to remove members inactive for 3mo 8d while making sure that the threshold remains above 75%. If the number of members falls below 8, the OpFoundationUpgradeSafe takes ownership of the multisig). Member of Optimism Guardian Multisig, SuperchainProxyAdminOwner.
- A Guardian Optimism Guardian Multisig
Participants (13):
0xE61F…76aE0x652B…cB5f0x5c1f…7a810x4A73…e61E0x3A53…aa940xEF9A…877c0x6323…c8650xd5b7…aC900x7ed8…9E390x0aA3…75D70x0a87…efE60xbfA0…E0d90x9282…cACbModular contract to be used together with the LivenessModule. Tracks liveness / activity of Safe owners.
- Can interact with LivenessModule
- can remove members of Optimism Security Council inactive for 3mo 8d
A Multisig with 1/1 threshold. It uses the following modules: DeputyPauseModule (Allows 0x352f1defB49718e7Ea411687E850aA8d6299F7aC, called the deputy pauser, to act on behalf of the OpFoundationUpgradeSafe if set as its Safe module).
Participants (1):
Optimism Security CouncilA Multisig with 2/2 threshold. Member of OpFoundationUpgradeSafe, OpFoundationOperationsSafe.
A Multisig with 5/7 threshold. It uses the following modules: SaferSafes (A Gnosis Safe module combining LivenessModule and TimelockGuard. Provides liveness checks where a fallback owner can challenge and take over if Safe owners are unresponsive, plus optional timelock delays for transaction scheduling).
- A Sequencer - acting directly
- A Guardian DeputyPauseModule though restricted to the SuperchainConfig’s
pause()function → Optimism Guardian Multisig
OP Mainnet
Actors:
A Multisig with 3/5 threshold.
- Can interact with MintManager
- change the OP token owner to a different MintManager and therefore change the inflation policy
- Can upgrade with no delay
- DeployerWhitelist ProxyAdmin
- L2CrossDomainMessenger ProxyAdmin
- GasPriceOracle ProxyAdmin
- L2StandardBridge ProxyAdmin
- SequencerFeeVault ProxyAdmin
- OptimismMintableERC20Factory ProxyAdmin
- L1BlockNumber ProxyAdmin
- L2ERC721Bridge ProxyAdmin
- L1Block ProxyAdmin
- L2ToL1MessagePasser ProxyAdmin
- OptimismMintableERC721Factory ProxyAdmin
- ProxyAdmin ProxyAdmin
- BaseFeeVault ProxyAdmin
- L1FeeVault ProxyAdmin
- OperatorFeeVault ProxyAdmin
- SchemaRegistry ProxyAdmin
- EAS ProxyAdmin

Ethereum
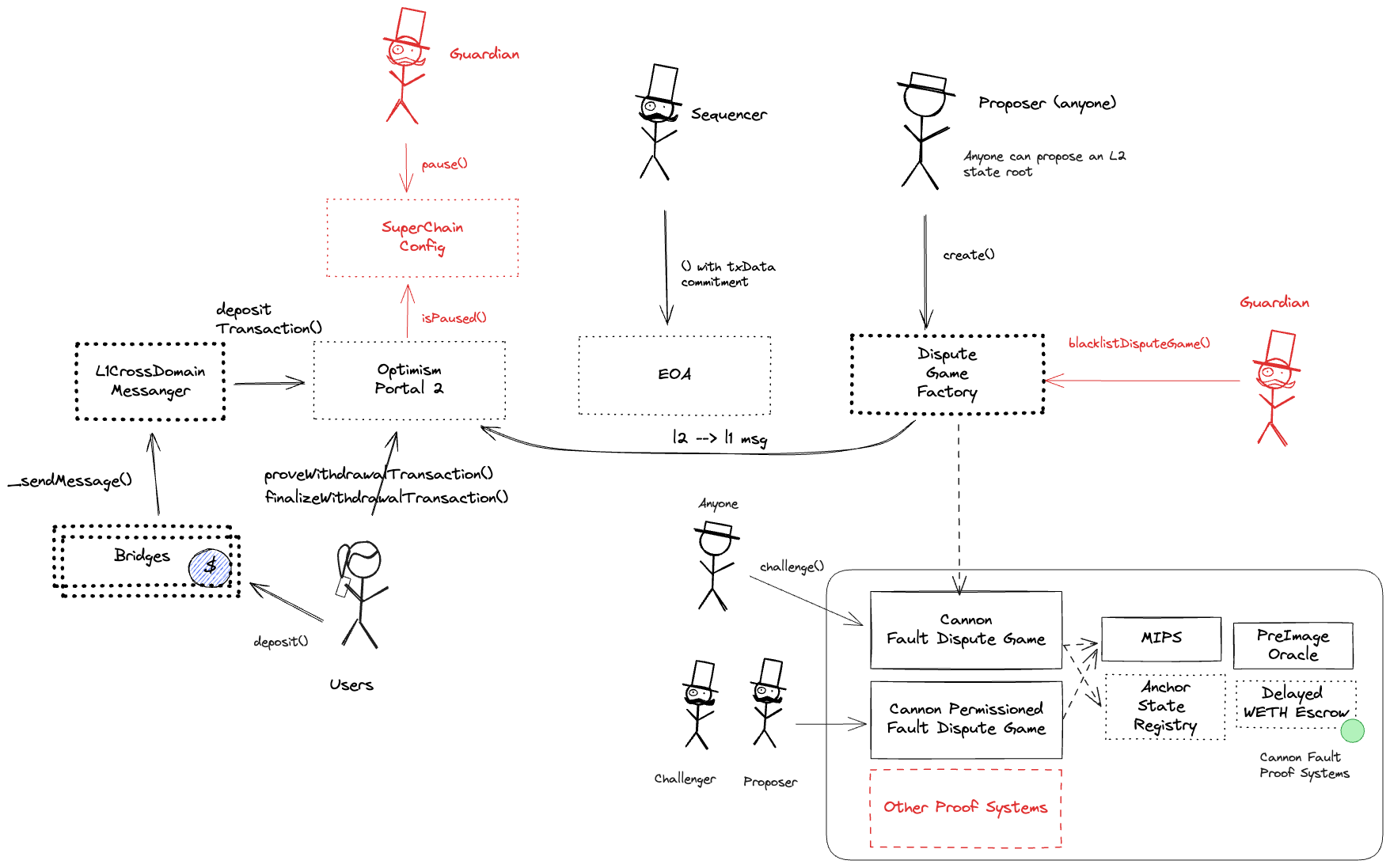
The OptimismPortal contract is the main entry point to deposit funds from L1 to L2. It also allows to prove and finalize withdrawals. It specifies which game type can be used for withdrawals, which currently is the FaultDisputeGame.
- Roles:
- admin: SuperchainProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner
The dispute game factory allows the creation of dispute games, used to propose state roots and eventually challenge them.
- Roles:
- admin: SuperchainProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner
Used to manage global configuration values for multiple OP Chains within a single Superchain network. The SuperchainConfig contract manages individual pause states for each chain connected to it, as well as a global pause state for all chains. The guardian role can pause either separately, but each pause expires after 3 months if left untouched.
- Roles:
- admin: SuperchainProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner
- guardian: Optimism Guardian Multisig; ultimately OpFoundationUpgradeSafe, Optimism EOA 1, Optimism Security Council, SaferSafes
Sends messages from host chain to this chain, and relays messages back onto host chain. In the event that a message sent from host chain to this chain is rejected for exceeding this chain’s epoch gas limit, it can be resubmitted via this contract’s replay function.
- Roles:
- admin: SuperchainProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner
Used to bridge ERC-721 tokens from host chain to this chain.
- Roles:
- admin: SuperchainProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner
The main entry point to deposit ERC20 tokens from host chain to this chain.
- Roles:
- admin: SuperchainProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner
- This contract can store any token.
used to remove members inactive for 3mo 8d while making sure that the threshold remains above 75%. If the number of members falls below 8, the OpFoundationUpgradeSafe takes ownership of the multisig
- Roles:
- fallbackOwner: OpFoundationUpgradeSafe if the number of Optimism Security Council members falls below 8
- livenessGuard: LivenessGuard
Custom Gateway for DAI deposits via canonical messaging. Deposited DAI is forwarded to a Vault contract.
The PreimageOracle contract is used to load the required data from L1 for a dispute game.
Contains the latest confirmed state root that can be used as a starting point in a dispute game. It specifies which game type can be used for withdrawals, which currently is the FaultDisputeGame.
- Roles:
- admin: SuperchainProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner
A simple escrow contract storing ETH for the canonical bridge.
- Roles:
- admin: SuperchainProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner
- This contract stores the following tokens: ETH.
Stores DAI deposited from the attached L1DAITokenBridge.
- This contract stores the following tokens: DAI, USDS, sUSDS.
Same as FaultDisputeGame, but only two permissioned addresses are designated as proposer and challenger.
Custom escrow for SNX bridged via canonical messaging.
- This contract stores the following tokens: SNX.
The MIPS contract is used to execute the final step of the dispute game which objectively determines the winner of the dispute.
Logic of the dispute game. When a state root is proposed, a dispute game contract is deployed. Challengers can use such contracts to challenge the proposed state root.
A helper contract that generates OptimismMintableERC20 contracts on the network it’s deployed to. OptimismMintableERC20 is a standard extension of the base ERC20 token contract designed to allow the L1StandardBridge contracts to mint and burn tokens. This makes it possible to use an OptimismMintableERC20 as this chain’s representation of a token on the host chain, or vice-versa.
- Roles:
- admin: SuperchainProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner
Lido custom escrow for wstETH tokens that uses the canonical bridge for messaging but is governed externally.
- This contract stores the following tokens: wstETH.
Allows 0x352f1defB49718e7Ea411687E850aA8d6299F7aC, called the deputy pauser, to act on behalf of the OpFoundationUpgradeSafe if set as its Safe module.
- Roles:
- deputy: Optimism EOA 1 though restricted to the SuperchainConfig’s
pause()function
- deputy: Optimism EOA 1 though restricted to the SuperchainConfig’s
Contract designed to hold the bonded ETH for each game. It is designed as a wrapper around WETH to allow an owner to function as a backstop if a game would incorrectly distribute funds.
- Roles:
- admin: SuperchainProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner
Contract designed to hold the bonded ETH for each game. It is designed as a wrapper around WETH to allow an owner to function as a backstop if a game would incorrectly distribute funds.
- Roles:
- admin: SuperchainProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner
OP Mainnet
The L2CrossDomainMessenger (L2xDM) contract sends messages from L2 to L1, and relays messages from L1 onto L2 with a system tx. In the event that a message sent from L2 to L1 is rejected for exceeding the L1 gas limit, it can be resubmitted via this contract’s replay function.
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner - L2 Alias
Contracts to register schemas for the Ethereum Attestation Service (EAS).
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner - L2 Alias
Contract containing the main logic for the Ethereum Attestation Service (EAS).
- Roles:
- admin: ProxyAdmin; ultimately SuperchainProxyAdminOwner - L2 Alias
The OP token contract. The minting policy is controlled by the MintManager.
Controls the OP inflation rate, which is currently hardcoded to 2% annually.
- Roles:
- owner: MintManagerOwner
Value Secured is calculated based on these smart contracts and tokens:
Main entry point for users depositing ERC20 token that do not require custom gateway.
Maker/Sky-controlled vault for DAI, USDS and sUSDS bridged with canonical messaging.
Main escrow for users depositing ETH.
SNX Vault for custom SNX Gateway managed by Synthetix.
wstETH Vault for custom wstETH Gateway. Fully controlled by Lido governance.
The current deployment carries some associated risks:
Funds can be stolen if a contract receives a malicious code upgrade. Both regular and emergency upgrades must be approved by both the Security Council and the Foundation. There is no delay on regular upgrades.
Program Hashes
Name | Hash | Repository | Verification | Used in | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0x033c...bb6e | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
